Rotational Motion of Solid Objects
... needs to be placed farther from the fulcrum than the larger weight for the system to be balanced, but it may not tell you how much farther (fig. 8.6). Trial and error with a simple balance will show that the smaller weight must be placed twice as far from the fulcrum as the larger (twice as large) w ...
... needs to be placed farther from the fulcrum than the larger weight for the system to be balanced, but it may not tell you how much farther (fig. 8.6). Trial and error with a simple balance will show that the smaller weight must be placed twice as far from the fulcrum as the larger (twice as large) w ...
Classical Mechanics and Human Movement
... gain insights into movement mechanics. Today, motion analysis finds particular use in physical education, professional sports, and medical diagnostics. Recent research suggests that the video recording of crawling infants may be used to diagnose autism at an early stage. The sequential photography a ...
... gain insights into movement mechanics. Today, motion analysis finds particular use in physical education, professional sports, and medical diagnostics. Recent research suggests that the video recording of crawling infants may be used to diagnose autism at an early stage. The sequential photography a ...
Solutions to Problems
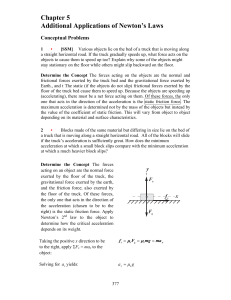
... The force required to produce the torque can be found from rF sin . The force is applied perpendicularly to the wrench, so 90o . Thus 88 m N F 3.1 10 2 N r 0.28 m (b) The net torque still must be 88 m N . This is produced by 6 forces, one at each of the 6 points. Those forces are a ...
... The force required to produce the torque can be found from rF sin . The force is applied perpendicularly to the wrench, so 90o . Thus 88 m N F 3.1 10 2 N r 0.28 m (b) The net torque still must be 88 m N . This is produced by 6 forces, one at each of the 6 points. Those forces are a ...