* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9-4,5,6,7
Sagnac effect wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Inertial frame of reference wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Routhian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Rigid rotor wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Tensor operator wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Accretion disk wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Moment of inertia wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Rotational spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
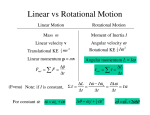
9.4. Newton’s Second Law for Rotational Motion A model airplane on a guideline has a mass m and is flying on a circle of radius r (top view). A net tangential force FT acts on the plane. NEWTON’S SECOND LAW FOR A RIGID BODY ROTATING ABOUT A FIXED AXIS Moment of Inertia of point masses Moment of Inertia, I for Extended regularshaped objects 9.5 Rotational Work and Energy Work and energy are among the most fundamental and useful concepts in physics. The force F does work in rotating the wheel through the angle q. ROTATIONAL WORK The rotational work WR done by a constant torque t in turning an object through an angle q is SI Unit of Rotational Work: joule (J) ROTATIONAL KINETIC ENERGY Demo on Rolling Cylinders 9.6 Angular Momentum The angular momentum L of a body rotating about a fixed axis is the product of the body's moment of inertia I and its angular velocity w with respect to that axis: SI Unit of Angular Momentum: kg · m2/s. CONSERVATION OF ANGULAR MOMENTUM The total angular momentum of a system remains constant (is conserved) if the net external torque acting on the system is zero. Demonstration on Conservation of angular momentum http://www.exploratorium.edu/snacks/momentum_machine.html Problem A woman stands at the center of a platform. The woman and the platform rotate with an angular speed of 5.00 rad/s. Friction is negligible. Her arms are outstretched, and she is holding a dumbbell in each hand. In this position the total moment of inertia of the rotating system (platform, woman, and dumbbells) is 5.40 kg·m2. By pulling in her arms, she reduces the moment of inertia to 3.80 kg·m2. Find her new angular speed.