Lab 5 Torque and Angular Acceleration
... Physical principles: Newton’s law of motion for rotation asserts that the net torque acting on an object equals the product of its moment of inertia and its angular acceleration. ...
... Physical principles: Newton’s law of motion for rotation asserts that the net torque acting on an object equals the product of its moment of inertia and its angular acceleration. ...
chapter eight solutions - Jay Mathy Science Wiki
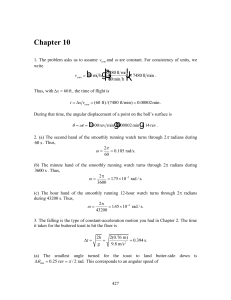
... First, apply the above equation about the x axis. We have, Ix = (3 kg)(9 m2)+(2 kg)(9 m2)+(2 kg)(9 m2)+(4kg)(9 m2) = 99.0 kg m2. About the y axis, we have Iy = (3 kg)(4 m2) + (2 kg)(4 m2) + (2 kg)(4 m2) + (4kg)(4 m2) = 44.0 kg m2. The distance, r, (from an axis through O and perpendicular to the pag ...
... First, apply the above equation about the x axis. We have, Ix = (3 kg)(9 m2)+(2 kg)(9 m2)+(2 kg)(9 m2)+(4kg)(9 m2) = 99.0 kg m2. About the y axis, we have Iy = (3 kg)(4 m2) + (2 kg)(4 m2) + (2 kg)(4 m2) + (4kg)(4 m2) = 44.0 kg m2. The distance, r, (from an axis through O and perpendicular to the pag ...
THEORETICAL MECHANICS
... the bodies in the time of the mechanical events. The mass in theoretical mechanics is the measure of the inertia of bodies in translation motion and will represent the quantity of the substance from the body, constant in the time of the studied phenomenon. Besides of these fundamental notions, theor ...
... the bodies in the time of the mechanical events. The mass in theoretical mechanics is the measure of the inertia of bodies in translation motion and will represent the quantity of the substance from the body, constant in the time of the studied phenomenon. Besides of these fundamental notions, theor ...
CHAPTER 8
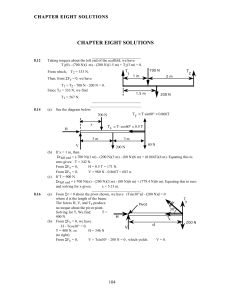
... 33. The force to produce the required torque is Fwrench = /L = (80 m · N)/(0.30 m) = 2.7 102 N. Because this torque is balanced by the torque produced by the bolt on the wrench, an equal torque is produced on the bolt. Because there are six points where a force is applied to the bolt, we have Fbo ...
... 33. The force to produce the required torque is Fwrench = /L = (80 m · N)/(0.30 m) = 2.7 102 N. Because this torque is balanced by the torque produced by the bolt on the wrench, an equal torque is produced on the bolt. Because there are six points where a force is applied to the bolt, we have Fbo ...
9.5. Particular motions of a rigid body
... propriety in the first part of this mechanics) as a non deformable and continuous system of particles. At the limit the number of these particles tends to infinity. This fact makes as the study of the motion of a body to solve in two ways: -In the first case are considered the points of the body and ...
... propriety in the first part of this mechanics) as a non deformable and continuous system of particles. At the limit the number of these particles tends to infinity. This fact makes as the study of the motion of a body to solve in two ways: -In the first case are considered the points of the body and ...
Momentum and Its Conservation
... Conservation of Momentum Propulsion in Space In a traditional rocket engine, the products of the chemical reaction taking place in the combustion chamber are released at high speed from the rear. In the ion engine, however, xenon atoms are expelled at a speed of 30 km/s, producing a force of only 0. ...
... Conservation of Momentum Propulsion in Space In a traditional rocket engine, the products of the chemical reaction taking place in the combustion chamber are released at high speed from the rear. In the ion engine, however, xenon atoms are expelled at a speed of 30 km/s, producing a force of only 0. ...
Exam 3 Review Questions PHY 2425 - Exam 3
... 12 A golf ball and a Ping-Pong ball are dropped in a vacuum chamber. When they have fallen halfway to the floor, they have the same A) speed. B) potential energy. C) kinetic energy. D) momentum. E) speed, potential energy, kinetic energy, and momentum. Ans: A Section: 8–2 Topic: Kinetic Energy of a ...
... 12 A golf ball and a Ping-Pong ball are dropped in a vacuum chamber. When they have fallen halfway to the floor, they have the same A) speed. B) potential energy. C) kinetic energy. D) momentum. E) speed, potential energy, kinetic energy, and momentum. Ans: A Section: 8–2 Topic: Kinetic Energy of a ...
class xi physics - Kendriya Vidyalaya No.1
... one out of three coordinates specifying the position of the object change with time. In such a motion an object move along a straight line path. *Two dimensional motion:- The motion of an object is said to be two dimensional motion if two out of three coordinates specifying the position of the objec ...
... one out of three coordinates specifying the position of the object change with time. In such a motion an object move along a straight line path. *Two dimensional motion:- The motion of an object is said to be two dimensional motion if two out of three coordinates specifying the position of the objec ...
Precession

Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In other words, the axis of rotation of a precessing body itself rotates around another axis. A motion in which the second Euler angle changes is called nutation. In physics, there are two types of precession: torque-free and torque-induced.In astronomy, ""precession"" refers to any of several slow changes in an astronomical body's rotational or orbital parameters, and especially to Earth's precession of the equinoxes. (See section Astronomy below.)