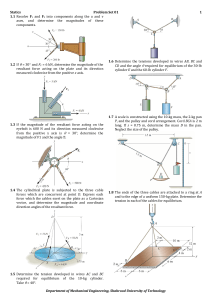
here.
... • A point particle moving along a wire in the shape of a line or circle has one degree of freedom, namely its position (coordinate) along the wire. A point particle moving in a central force field has three degrees of freedom, we need three coordinates to specify the location of the particle. The Ea ...
... • A point particle moving along a wire in the shape of a line or circle has one degree of freedom, namely its position (coordinate) along the wire. A point particle moving in a central force field has three degrees of freedom, we need three coordinates to specify the location of the particle. The Ea ...
Chapter 11
... 14. To find the center of mass speed v on the plateau, we use the projectile motion equations of Chapter 4. With voy = 0 (and using “h” for h2) Eq. 4-22 gives the time-offlight as t = 2h/g . Then Eq. 4-21 (squared, and using d for the horizontal displacement) gives v2 = gd2/2h. Now, to find the spee ...
... 14. To find the center of mass speed v on the plateau, we use the projectile motion equations of Chapter 4. With voy = 0 (and using “h” for h2) Eq. 4-22 gives the time-offlight as t = 2h/g . Then Eq. 4-21 (squared, and using d for the horizontal displacement) gives v2 = gd2/2h. Now, to find the spee ...
Chapter 9 Rotational Motion
... In the analysis of rotational motion, we will see a great similarity to translational motion. In fact, this chapter can serve as a review of all the mechanics discussed so far. Also since the student should now have become more mature mathematically than in the beginning of the course, we will use m ...
... In the analysis of rotational motion, we will see a great similarity to translational motion. In fact, this chapter can serve as a review of all the mechanics discussed so far. Also since the student should now have become more mature mathematically than in the beginning of the course, we will use m ...
Extra problems similar to final:
... 19) The velocity of an airplane with respect to the ground is 200 m/s at an angle of 30 degrees NORTH of EAST. The velocity of the airplane with respect to the air is 150 m/s at an angle of 60 degrees NORTH of EAST. What is the velocity of the air with respect to the ground? a) 158 m/s at 16.9 degre ...
... 19) The velocity of an airplane with respect to the ground is 200 m/s at an angle of 30 degrees NORTH of EAST. The velocity of the airplane with respect to the air is 150 m/s at an angle of 60 degrees NORTH of EAST. What is the velocity of the air with respect to the ground? a) 158 m/s at 16.9 degre ...
Precession

Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In other words, the axis of rotation of a precessing body itself rotates around another axis. A motion in which the second Euler angle changes is called nutation. In physics, there are two types of precession: torque-free and torque-induced.In astronomy, ""precession"" refers to any of several slow changes in an astronomical body's rotational or orbital parameters, and especially to Earth's precession of the equinoxes. (See section Astronomy below.)