* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name
Deep sea fish wikipedia , lookup
Atlantic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
El Niño–Southern Oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
Challenger expedition wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
History of research ships wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean Research Group wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
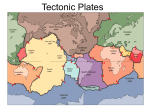
Name: ________Answer Key__________________________ Date: _________________________________ Block:_____ Exploring the Oceans Study Guide 1. Know the features of the topography of the ocean floor. Use pages 384 – 385 of your textbook. 2. Know what sonar stands for and how sonar works. Sonar stands for sound navigation and ranging. Scientists send sound pulses from a ship down into the ocean. The sound moves through the water, bounces off the ocean floor and returns to the ship. 3. Be able to explain why you think that geological features in the ocean are bigger than the ones on land. The geological features on the ocean floor are bigger because they do not have the weathering and erosion that takes place on land. 4. How did water form on Earth? The Earth cooled enough for water vapor to condense. 5. The ocean helps to regulate temperatures. How does this help with regulating temperatures between day and night, and how does it help in regulating temperatures at different locations? If the ocean did not regulate the temperatures, there would be a great difference in temperatures between the day and night. The temperatures are different with the different locations. 6. What is salinity? A measure of the amount of dissolved solids in a given amount of liquid. 7. Explain the variation of temperature with latitude and time of year. Depending on the time of year and latitude, it determines the temperature of the ocean. 8. Explain salinity with regard to climate: for example, hot, dry climate, what would be the salinity of the ocean? If the climate is hot and dry, the salinity of the ocean would tend to have high salinity. 9. Which zone is located between the high- and low-tide limits? The Intertidal Zone 10. Define the Water Cycle. The movement of water from ocean to the atmosphere to the land and back to the ocean. 11. When using sonar, what might it mean if it takes a long time for the sound wave to return to the ship? If it takes a long time for the sound wave to return, it is very deep. 12. What are the two zones in the pelagic environment? Neritic Zone and Oceanic Zone 13. What are the two major regions of the ocean floor? Continental Margin and Deep-Ocean Basin 14. How are the regions of the continental margin divided? By depth and slope 15. What does the ocean help to regulate and how does it regulate it? Temperatures around the Earth.