* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download republic_government
Structural history of the Roman military wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Factorum ac dictorum memorabilium libri IX wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Centuriate Assembly wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Roman tribe wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Leges regiae wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
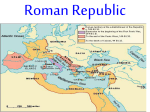
Name __________________________ Roman Republic Info Sheet REPUBLICAN GOVERNMENT Date 753 BCE 509 BCE Type of Government MONARCHY - City of Rome founded by Romulus and Remus – Romulus killed Remus and named the city after himself. City falls under the control of Etruscan kings. REPUBLIC – Romans overthrow the last Etruscan king and want to avoid one leader with complete control. The Roman Republic will last until the reign of Augustus. Social Class in Rome Plebeians – Small land owners, craftsmen, small Patricians – Large landowners and the ruling class farmers and merchants of Rome. They were of the Roman Republic. They were the only class citizens, but they could not be elected to office. allowed to be elected consul, senator, or any of They may not marry the Patricians but are the other major offices listed below. expected to fight in the Roman army. If they have the same responsibilities of Patricians, they wondered, then why not the same rights? Government of the Roman Republic Executive Branch Legislative Branch Consuls – Two officials selected each year. These Senate – Three hundred men (900 when Julius men ran the government and lead armies. Caesar is in power and expands the Senate) elected for life. Originally convened to advise Praetors – In charge of laws for Roman citizens. public officials, but in time, their decrees were Later, some praetors handled cases dealing with treated as laws. noncitizens. These men were elected for one year. Centuriate Assembly – Based on wealth, and in Quaestors – Financial officers that dealt with the this case the upper class citizens were in the treasury. These men were elected for one year. majority. These men decided when Rome was involved in war and also elected higher government Aediles – Maintained public buildings. These men officials. were elected for one year. Council of the Plebs – Started in 471 BCE, but its Tribunes of the Plebs – Ten men elected for one decrees were not binding to all citizens until 271 year, called meetings of the Council of Plebs. BCE. After years of arguing, the Council of the Plebs was formed to protect Plebeians. Later, Censors – Two elected for eighteen months. Plebs were allowed to marry Patricians, become These men conducted the census of goods and consul, and by 271 BCE they could pass laws for all citizens. Romans. The Twelve Tables In 450 BCE, in response to the demand of the Plebeians for equal rights, the Patricians agreed to pass the Twelve Tables. These twelve laws were engraved on bronze tables and displayed in the Roman Forum, the center of the city. These laws covered property rights, the right to trials, inheritance rights, etc. Before the creation of the Twelve Tables, law was determined by the Patricians. Roman Expansion Rome conquered the tribes surrounding the city and continued to expand its territory. Rome continued to conquer the lands in the Italian Peninsula and expand around the Mediterranean, coming into contact with a major power to the south, Carthage.