* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8 Study Guide (7th Grade Science) Lesson 8.1 *An
Survey
Document related concepts
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Old-growth forest wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
List of ecoregions in North America (CEC) wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Tropical rainforest wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath: Population Zero wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
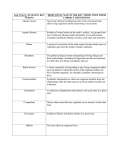
Chapter 8 Study Guide (7th Grade Science) Lesson 8.1 *An organism gets food, water, shelter, and other tings it needs to live, grow, and reproduce from its environment. Organism-a living thing Habitat-an environment that provides the things a specific species needs to live, grow, and reproduce *An organism interacts with both the living and nonliving parts of its habitat. Biotic factor-the living or once living parts of an organism’s habitat Abiotic factor-the non-living parts of an organism’s habitat Species-a group of organisms that can mate and have a fertile offspring Population-all the members of one species that live in a particular area Community-all the different populations that live together in an area Ecosystem-the community of organisms, along with the nonliving environment *In ecosystems, the smallest level of organization is the organism, which belongs to a population that includes other members of its species. The population belongs to a community of different species. The community and abiotic factors together form an ecosystem. organismpopulationcommunityecosystem Ecology-the study of how organisms interact with each other and w/ their environment Lesson 8.2 *Two major types of interactions among organisms are competition and predation. Niche-the role an organism plays in its habitat; this includes what type of food it eat, how it obtains its food, what predators eat the organism, when and how it reproduces, and the physical conditions it requires to survive. Competition-the struggle between organisms to survive as they attempt to use the same limited resources Predation-an interaction where one organism kills another for food or nutrients Predator-the organism that does the killing in predation Prey-the organism that is killed in predation Symbiosis-any relationship in which two species live close together and at least one of the species benefits; known as a symbiotic relationship Mutualism-a type of symbiotic relationship where both species benefit Commensalism-a type of symbiotic relationship where only one benefits, but the other is not harmed Parasitism-a type of symbiotic relationships where one organism (the parasite) lives with, on, or inside another organism (the host), harming the host Parasite-the organism that benefits from a parasitic relationship Host-the harmed organism that the parasite lives in or on, in a parasitic relationship **Be able to recognize and/or give your own specific examples of biotic and abiotic factors, competition, predator-prey interactions, and the three forms of symbiosis. Refer to textbook examples if you need help. Lesson 8.3 *The 6 major biomes are desert, rain forest, grassland, deciduous forest, boreal forest, and tundra. Biomes-a group of ecosystems with similar climates and organisms Climate-the average annual conditions of temperature, precipitation, winds, and clouds in an area Desert-a dry region that on average receives less than 25 cm. of precipitation per year Rain forest-a forest that receives at least 2 meters of rain per year, mostly occurring in the tropical wet climate zone Emergent layer-the tallest layer of the rain forest that receives the most sunlight Canopy-a leafy roof formed by tall trees I a rain forest Understory-a layer of shorter trees and vines that grows in the shade of a forest canopy Grassland-an area populated by mostly grasses and other non-woody plants that gets 25-75 cm of rain each year Savanna-a grassland located close to the equator that may include shrubs and small trees and receives as much as 120 cm of rain per year Deciduous tree-a tree that sheds its leaves during a particular season and grows new ones each year Boreal forest-dense forest of evergreens located in the upper regions of the Northern Hemisphere Coniferous tree-a tree that produces its seeds in cones and that has needle shaped leaves coated in a waxy substance to reduce water loss Tundra-an extremely c old, dry biome climate region characterized by short, cool summers and bitterly cold winters Permafrost-permanently frozen soil found in the tundra biome Lesson 8.4 *There are two types of aquatic (water-based) ecosystems: freshwater ecosystems and marine (saltwater) ecosystems. *All aquatic ecosystems are affected by 4 abiotic factors: sunlight, temperature, oxygen, salt content. Estuary-a kind of wetland formed where fresh water from rivers mixes with salty ocean water Intertidal zone-an area between the highest high-tide line on land and the point on the continental shelf exposed by the lowest low-tide line Neritic zone-the area of the ocean that extends from the low-tide line out to the edge of the continental shelf Freshwater ecosystems include streams, rivers, ponds, and lakes. Marine ecosystems include ocean zones (intertidal, neritic, surface ocean, deep ocean). Webquest Answers Tundra -characterized by very low temperatures, permafrost, very little precipitation (rain or snow), a short growing season, few nutrients, and low biological diversity. The word tundra comes from the Finnish word tunturia, which means "treeless plain." Rain Forest –typically very dense, warm, wet forests. They are havens for millions of plants and animals. Temperate rain forests receive a lot of rain, but have moderate temperatures. Tropical rain forests are found in areas close to the equator. This has typical rain forest climate. Boreal forest (Taiga) -cold woodland or forest. This biome spans the northern parts of North America, Europe, and Asia; coniferous trees, such as spruce and fir, grow here Grassland (Prairie)- an area populated by mostly grasses and other non-woody plants that gets 25-75 cm of rain each year; home to many of the largest animals on earth Savannas (Tropical grassland) - hot all year with wet seasons that bring torrential rains. Located near the equator. Deserts -harsh environment with very little rainfall and extreme temperatures; organisms that live here must be adapted to little or no rain and extreme temps. Temperate deciduous forests -forests with varying temperatures; have four distinct seasons; deciduous trees grow here An ecosystem includes soil, atmosphere, heat and light from the sun, water and living organisms. Producers include green plants. They make their own food. Consumers are animals and they get their energy from the producers or from organisms that eat producers. The three types of consumers are herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores. Herbivores are animals that eat plants. Carnivores are animals that eat herbivores and sometimes other carnivores. Omnivores are animals that eat plants and other animals. Bees have a symbiotic relationship with the flowers they pollinate. A symbiotic relationship is one that benefits both living things. For example, bees get the nectar they need and the flowers get pollinated. Carnivores keep balance in a community by helping control population size. This is the carnivore's niche. Decomposers are plants and animals that break down dead plants and animals into organic materials that go back into the soil. Examples are bacteria, fungi, and earthworms. Scavengers eat carrion, or dead animals. They help break down or reduce organic material into smaller pieces. These smaller pieces are then eaten by decomposers. Three abiotic factors that limit population are the availability of food, water and shelter Two biotic factors that limit population size are predators and humans. Disease can also impact populations.