* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology Unit Test Study Guide
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of the San Francisco Estuary wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
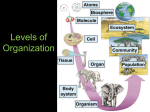
Name: Date: No. Ecology Unit Test Review Guide (Turn in COMPLETED on test day, BEFORE the test for bonus points on the test!) 1. List the levels of organization within the environment from largest to smallest (most specific). 2. What level of organization would describe a flock of pigeons in a park? 3. Complete a Venn Diagram comparing and contrasting biotic and abiotic factors. 4. Label each of the following A (abiotic) or B (biotic). Deer Carbon 5. rocks phosphorus water plants fungi bacteria Complete the table below that describes the 2 processes responsible for cycling energy through the ecosystem. Process Reactants Products Organelle responsible Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration 6. 7. Differentiate between a food chain and a food web. Describe the niche (job/role) of each of the following: 8. a. Producer b. Consumer c. Herbivore d. Carnivore e. Omnivore f. Detritivore (decomposer) What is an energy pyramid? 9. Label the trophic levels in the energy pyramid below. 10. What happens to the amount of energy as you move up the pyramid? What percentage actually passes from one trophic level to the next? 11. Use the marine food web on page 410 in the textbook. Choose ONE food chain from this food web. Copy the food chain and label the organisms as producers, consumers, and/or decomposers. 12. Provide a generalized flow chart for each of the following abiotic cycles (You have something like this in your NOTES!) a. Water cycle b. Carbon cycle c. Phosphorus cycle d. Nitrogen cycle 13. How does habitat differ from niche? 14. Label each of the following as N (niche) or H (habitat). 15. Predator savanna Herbivore decomposer Complete the following table about symbiosis Relationship lake tundra Describe what happens to each member Mutualism Parasitism Commensalism 16. 17. How does each of the following affect population size? a. Immigration b. Birth c. Emigration d. Death Sketch graphs for each of the following types of population growth: a. Exponential growth (Be sure to label each axis) b. Logistic growth (Be sure to label each axis) ocean forest Example 18. Complete the table below: Limiting Factors Density-Dependent Factors Definition Examples Density-Independent Factors 19. Differentiate between primary and secondary succession. 20. List the six terrestrial biomes. 21. List the 3 aquatic ecosystems. What are the 4 oceanic zones? 22. Compare and contrast renewable and nonrenewable resources. List 3 examples of each. 23. 24. 25. What is person’s ecological footprint? What are some things they can do to reduce their footprint? How does air pollution contribute to global warming? Explain how predation and competition are important ways in which organisms can interact. Ecology Vocabulary Review Across 8. a symbiotic relationship in which both organisms benefit 9. resources that can replenish themselves over time 12. area where an organism lives 13. movement of individuals into a population 15. examples include tundra, taiga, grasslands, desert, etc. 16. organisms that eat only plants 18. model that shows the complex network of feeding relationships and flow of energy within an ecosystem 19. partially enclosed body of water formed where a river flows into an ocean 21. factors that are nonliving things Down 1. a symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits, but the host organism is harmed 2. group of the same species that lives in one area 3. group of different species that live together in one area 4. any undesirable factor added to air, water, or soil 5. sequence of biotic changes that regenerate a damaged community 6. organisms that eat only animals 7. organisms that eat plants and animals 10. movement of individuals out of a population 11. resources that are used faster than they form 14. a symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is not affected 17. factors that are living things 20. an organism's role in the environment