* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology Notes 4-2
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
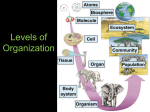
Ecology Notes 4-2 Community Interactions Biotic vs. Abiotic Biotic factors – living factors in an environment. Ex. Trees, birds, bacteria, etc. Abiotic factors – non living factors in an environment. Ex. Temp., rainfall, humidity, soil. Niche Niche – full range of conditions in which an organism lives (biotic and abiotic). It is like your “occupation”. Competition Competition – occurs when organisms attempt to use a resource (water, nutrients, light, food or space) at the same time. We call this a +/- relationship. Competitive Exclusion Principle – no two organisms can occupy exactly the same niche in the same habitat at the same time. Predation One organism captures and feeds on another organism. This is a +/relationship. Symbiosis – any relationship where two organisms live closely together. 3 types of Symbiosis 1. Mutualism +/+ both organisms benefit. Ex. Flowers/insects. 2. Commensalism +/0 one organism benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed. Ex. Whales/barnacles 3. Parasitism +/- One organism lives on or in another organism. Ex. Dog/flea