* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ecology Notesheet
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
History of wildlife tracking technology wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
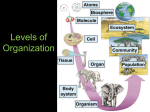
Ecology Chapter 3 & 4 Name: Biology 5.0 Date: Period: Chapter 3: Biosphere 3-1 What is ecology? • Ecology: the study of • Interdependence: Levels of Organization 1. Biosphere: largest level, our ________________, portions of planet where ____________ exists (land, H2O, air) - _________ above to _________ below 2. Biome: group of ecosystems that share _______________ _______________ (temp. and rainfall) 3. Ecosystem: collection of all in a particular place together with the environment. 4. Community: groups of populations that live together in a area species that live in area. 5. Population: groups of individuals of the 6. Species: group of organisms that can Biotic and Abiotic Factors Biotic – and produce fertile . part of the environment o Examples: Plants, Animals, Mold, Fungi, Bacteria, Protist Abiotic – part of the environment o Examples: Sunlight, heat, soil, wind, water, temperature Environment or Habitat – all conditions or factors includes both and an organism; factors. 3-2 Energy Flow • At the core of every organism’s interaction with the environment is its need for to power life’s processes Producers (_________________________) Use solar or chemical into complex organic molecules o Plants to produce by assembling inorganic compounds o Some _____________________ o Some _____________________ • • Photosynthesis: captures energy and converts it to energy Chemosynthesis – energy used to produce carbohydrates • Example: bacteria in harsh environments such as deep sea volcanic vents or hot springs 1 Consumers (_________________________) • Can’t trap energy directly; must acquire it from other ____________ Herbivores – eat Carnivores – eat other Omnivores – eat both and Scavengers – consume of other animals Decomposers – break down leaves, roots, or matter – produces detritus (small pieces of dead and decaying plant and animal remains) Detritivores – feed on 3-3 Energy Flow in Ecosystems Feeding Relationships ______________ ______________ ______________ Food Chain – energy Food Web – relationship more complex than a chain by passed on when organisms eat and are eaten Trophic Levels: each step in a food chain/web • Ex: then Ecological Pyramids – shows relative amount of Biomass – total amount of living at each trophic level within a trophic level 3-3 BioGeoChemical Cycles *Recycle Matter* Photosynthesis – CO2 from atmosphere; happens in the 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 Respiration – CO2 to atmosphere; happens in the C6H12O6 + O2 H2O + CO2 2 Carbon Cycle 1. Volcanoes, respiration, fossil fuels, and decomposition add ______________ to atmosphere. Organic carbon is locked deep beneath the Earth’s _____________ – high pressure converts layers of sediment (dead organisms and waste) to carbon-rich ______________________. Fossil fuels are extracted and processed to make _______________ and __________ –burning fossil fuels release _____________ 2. Plants take CO2 and make ____________________ 3. Plants are eaten by animals, carbohydrates are passed through the _____________________________ 4. As the animal breathes and eventually dies and _______________, CO2 is returned to the ______________ Water Cycle 1. How does water enter the atmosphere? __________________________ - water changes from a ___________ to a __________________ __________________________ - evaporation through _____________________ 2. As water rises, it cools and _________________ into tiny droplets that form _______________ 3. Droplets return to the earth as __________________ 4. Water __________ the rivers, ground water, ocean or plant roots to _______________ the cycle. Nitrogen Cycle 1. Nitrogen gas makes up ___________ of atmosphere 2. ____________________________ - bacteria take nitrogen gases and turn it into ___________________, nitrite, and nitrate. 3. Plants and animals use _____________ to make _______________ acids. 4. Animal dies and decomposes returning nitrates to the ________________. 5. _________________________ - other bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen _____________. 3 Phosphorus (as phosphate) Cycle • Phosphate – parts of ____________/____________ • Found in ____________that are worn down • Washes into rivers/streams/oceans for __________________ organisms • Taken in by _____________ and turned into organic compounds Nutrient Limitation • Primary Productivity – the rate at which _________________molecules are created by _________________ • If nutrients are in short supply, they are called _________________ _________________ Ex: Nitrogen is often limiting in water; if there is suddenly as input of N (fertilizer runoff), organisms can grow rapidly (Algal Bloom) 4 Chapter 4: Ecosystems and Communities 4-1 The Role of Climate • Climate: -term, over entire o Weather: • area -term, Greenhouse Effect • CO2, H2O, CH4 all trap • Keeps the and hold it next to the suitable for The Effect of Latitude on Climate • Earth has 3 climate zones due to unequal heating because of the angle of the sun – ___________________________ – ___________________________ – ___________________________ Heat Transport • Ocean and wind _____________ help produce Earth’s climates • They are affected by _____________ and Earth’s ____________ 4-2 Niches and Community Interactions The Niche o _____________ and _____________ something lives; the way the species obtains what it needs to _________________ and _________________. Habitat is the general place where an organism live ( Niche is the organism’s how it interacts with biotic and abiotic factors ( ) ) Community Interactions 1. Competition • Organisms compete for . Examples: ____________________________________________________ • Competitive Exclusion Principle – no 2 organisms occupy the habitat at exactly the niche in exactly the time. 2. Predation • One organism (___________) captures and feeds on another (_____). 5 3. Symbiosis • Mutualism – both species Examples: • Commensalism – one , the other is not nor Examples: • Parasitism – one , other is Examples: 4.3 Ecological Succession Ecological Succession - change in an 1. ____________________ Succession – no remnants of an older community (volcanic eruption or bare rock) 1st to colonize barren areas are called Examples: -composite, symbiotic organisms 2. ____________________ Succession – disturbance affects the community - soil exists (wild fires, clear cutting, plowed for farming) 3. Climax Community – fairly , dominant community established after 4-4 Land Biomes 6