* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earthquakes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
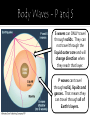
Earthquakes Chapter 12 Section 1 Earthquakes are movements of the ground caused by a sudden release of energy when rocks along a fault move. Seismology – the study of earthquakes and seismic waves Earthquakes can occur at plate boundaries or along fault lines in Earth’s crust. A fault is a break in a body of rock along which one block slides relative to one another. Earthquakes typically occur along transform boundaries when tectonic plates slide past one another. However, the strongest earthquakes occur at convergent boundaries due to the amount of increased stress on the rock. Earthquakes can be felt over large areas although they usually last less than one minute. FOCUS: the location within Earth along a fault line where the first motion of an earthquake occurs. (point of origin) EPICENTER: the point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus. During an earthquake rocks release energy in the form of vibrations called seismic waves There are TWO categories of SEISMIC WAVES Body waves – travel through the Earth primary and secondary waves Surface waves- travel along the Earth’s surface Love and Rayleigh waves Primary Waves (P waves) Fastest Travels through solids, liquids and gases First waves to be detected during an earthquake Moves rock back and forth, which stretches and squeezes the rock. Longitudinal wave Secondary Waves (S waves) Slower than P waves Second waves to be detected during an earthquake Stretches rock moves rocks side to side Travels ONLY through solids (can not travel through Earth’s outer core) Transverse wave S waves can ONLY travel through solids. They can not travel through the liquid outer core and will change direction when they reach that layer. P waves can travel through solid, liquids and gasses. That means they can travel through all of Earth’s layers. Slowest moving waves Can cause the most damage during an earthquake There are two types of Surface Waves Love Waves (L) – side to side motion Rayleigh Waves (R) – rolling elliptical motion Brain Pop: Earthquakes Discovery Education: Earthquakes