* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earthquake Resistant Buildings
Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Plant wikipedia , lookup
Casualties of the 2010 Haiti earthquake wikipedia , lookup
2008 Sichuan earthquake wikipedia , lookup
2011 Christchurch earthquake wikipedia , lookup
2010 Canterbury earthquake wikipedia , lookup
1908 Messina earthquake wikipedia , lookup
2009–18 Oklahoma earthquake swarms wikipedia , lookup
April 2015 Nepal earthquake wikipedia , lookup
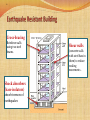
2010 Pichilemu earthquake wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake engineering wikipedia , lookup
1906 San Francisco earthquake wikipedia , lookup
1992 Cape Mendocino earthquakes wikipedia , lookup
1960 Valdivia earthquake wikipedia , lookup
Seismic retrofit wikipedia , lookup
1880 Luzon earthquakes wikipedia , lookup
By Hassan Mohamed Hassan Ismiel Khalid Hosni Khalid Salama Hamada Mahmoud 2 1.What is an earthquake ? 2.When do Earthquakes occur ? 3.Types of Shockwaves . 4.Methods to Reduce the Impacts of Earthquakes . 5.Conclusion . 3 The earthquake is the sudden release of some stored energies in the earth’s crust . 4 5 The shockwaves are called seismic waves. Some types of seismic waves are called body waves. The other waves are called surface waves. There are two different types of surface waves: Rayleigh waves and Love waves . 6 Problem : The collapse of infrastructure causes much economical damage and even deaths! 7 4.1.Planning the location of infrastructure: Build new infrastructure away from earthquake prone areas to reduce economical damage and lower number of deaths caused by earthquakes . Authorities can implement guidelines on the location of new infrastructure and set limits on the heights of buildings . 8 Buildings are not too tall in earthquakeprone Japan! 9 4.2.Designing Earthquake-Resistant Infrastructure: New infrastructure can be specially designed to withstand strong tremors by making use of the latest technology . 4.3. Strengthening Existing Infrastructure: New infrastructure can be specially designed to withstand strong tremors and reduce damage from earthquakes by making use of technology . 10 Cross-bracing Reinforce walls using two steel beams . Shock absorbers (base isolators) absorb tremors of earthquakes Shear walls (concrete walls with steel bars in them) to reduce rocking movements . 11 Existing infrastructure can be reinforced by wrapping steel frames around the pillars of buildings and bridges, or by placing steel rods in existing structures . 12 4.4. Education on Emergency Procedure: •Earthquake drills are conducted regularly in many earthquake-prone countries to educate and familiarize people on what to do in the event of an earthquake . •Governments of earthquake-prone countries also use posters and signs to warn people about areas that are prone to the effects of earthquakes e.g. coastal areas where tsunamis can occur . 13 The society needs to be educated on the advantages of the earthquake resistant construction. There is a need to disseminate earthquake engineering information in local languages in the manner that sustains the interests of common man. This will facilitate the better appreciation of earthquake safety. THUS IT IS ALWAYS SAID THAT, “PRECAUTION IS BETTER THAN CURE”.