* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Climate
Hyperthermia wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Lockheed WC-130 wikipedia , lookup
Water vapor wikipedia , lookup
Air quality law wikipedia , lookup
Cold-air damming wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric circulation wikipedia , lookup
Weather lore wikipedia , lookup
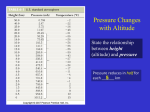
Climate & Meteorology I. Climate – The weather conditions, including temperature, precipitation and wind that characteristically occur in a particular region. A. An area’s ________________________________________________________________________________ Factors that affect climate – 1. ____________________________ 2. ____________________________ 3. ___________________________________________ 4. Marine vs. _______________________________ 5. ___________________________________ Effect 1. Latitude and Insolation a) Higher latitudes have __________________________ temperatures, because they receive less direct _______________________________. (1) _______________________ insolation – (a) Short daylight periods, ______________ shadow. (2) ____________________ insolation – (a) Long daylight periods, ______________-________ shadows. b) A Y T ____________________ yearly temperatures (____________) (1) Mathematical average of temperature measurements taken every day for one year. (2) 0o As ______________________________________________________ , ___________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ Lat. 90o c) Yearly Temperature _________________________ (YTR) (1) ________________________ and __________________________ temperatures for a particular area during a ____________ period. (2) As _____________________________________________________________________________, _____________________________________________________________________________ Temperature 0oLatitude 40o Latitude 90o Latitude Yearly Temp. Range 0o Lat. 90o JFMAMJJASOND 2. Altitude - ______________________________ especially _________________________________________ or above the Earth’s surface. a) As ________________________________________________________________________, _______________________________________________________. 3. _______________________________________________ - make the climate of ______________________ regions warmer or cooler __________________________________________ for that latitude. o Pg __________ of ESRT’s Warmer or Colder Than Normal? East Coast of N.A. ______________________ East Coast of S.A. _______________________ ___________________________ Current 4. Marine vs. Continental – a) Summer ___________________________________________ and loses heat much _________________ than water. Winter (1) Land areas tend to have: (a) ______________________________________________________ and _________________________________________________________. (b) Continental climates have ______________________________________ _______________________________ (2) __________________________________________; near large bodies of water tend to have: (a) _________________________________________________________ and ____________________________________________________. (b) Marine climates have ________________________________. 5. Orographic Effect and __________________________________________ Effect a) Caused by mountain ranges or coastal areas of higher elevation. (1) Orographic Effect - __________________________________________ side_ (a) _______________________ and ______________________ temperatures (i) (2) ______________________, Hawaii, Amazon Valley Rain Shadow Effect - ________________________________side (a) ______________________ and _______________________ temperatures (i) _______________________________, deserts of Peru 5. 4. 6. 3. 7. 2. 8. 1. B. Factors that Affect Rainfall – 1. Latitude - __________________________________________________ produces global _____________ and air _________________________________ belts. 2. a) Low pressure belts produce ________________ regions. b) High pressure belts produce _____________________ regions. (1) Wet latitudes are: ____________________________________________ (2) Dry latitudes are: _____________________________________________ Areas of Rainfall – a) Regions on Earth where air _________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________, forms clouds and precipitates. (1) ________________________________ side of a mountain (2) _________________________________ - ___________________________________ regions where warm humid air rises as a result of ____________________________. (a) Dry Produces thunderstorms almost __________________________. Wet Dry b) Regions on Earth where prevailing _______________________ blow in ______________ ____________________________________________; usually receive more rainfall. 3. Areas of __________________ rainfall – a) Regions on Earth where air _________________________________________________________ ____________________ and becomes less humid/______________. b) (1) ________________________________________ side of mountain (2) Horse (mid) latitudes - __________________________________ (3) High pressure weather systems Regions on Earth where _______________________________________ winds blow from the interior of a _____________________________________________; usually receive less rainfall. C. Region/Climate Comparison 1. Death Valley, California - ___________________________ 2. Cherrapunji, India - ________________________________ 3. Amazon Valley, South America - ____________________________ 4. Deserts of Peru, South America - ________________________________________________________ My Climate Weather vs. Climate Daily Weather Characteristics Meteorology: The scientific study of the atmosphere that focuses on ____________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________. II. Weather – The state, or ____________________________________, of atmospheric _____________________________ for a location at _______________________________________________ A. B. Atmospheric Variables & Measurements: 1. ________________________________ ___________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________ ___________________________________________________ 3. ________________________________ ___________________________________________________ 4. ________________________________ __________________________ or inches of Mercury Causes of Weather: 1. Amount of ___________________________________ (INcoming SOLar radiATION.) a) _________________ b) __________________ 2. __________________________________________________ of Earth’s surface. a) Surface heating is dependent on ___________________________________________________ of sunlight. LLLLL Low Latitude b) Mid Latitude High Latitude The uneven heating of Earth’s surface causes the ______________________________ to react and ________________________________ and infinite variety of weather _____________________________________. C. Weather Instruments: _____________________ Wet Bulb Dry Bulb Measures Air___________________ Relative _____________________ Measures Rainfall Measures & _______________________________________ _____________________ Measures ____________________________ _____________________ Measures __________________________ _____________________ Measures __________________________ III. Atmosphere - The shell of air (__________________________) that surrounds the Earth. A. B. Molecular Composition of the Atmosphere 1. 78% - __________________ 2. 21% - __________________ 3. 0-4% - ______________________ 4. 0.93% - Argon 5. .03% - __________________ 6. .01% - ____________________________ gases; ex. ______________________________ 7. Dust particles ( ____________________________________________________________________) Composition vs. Altitude: 1. 50 miles - From Earth’s surface to the Stratopause there is a mixture of gases including __________________________________________________________________________. 2. 600 miles - between the Mesosphere and the Ionosphere there is a layer of Oxygen and then a layer of Helium. 3. _______________miles - At the top of the Ionosphere there is a layer of Hydrogen that thins out into space. C. Temperature vs. Altitude: page ______ of ESRT. D. The Atmosphere & Insolation: Our Heat Budget 1. 6% - Reflected by ______________________, dust particles and water droplets 2. 20% - ______________________________ by clouds. 3. 4% - Reflected by _______________________________________________. 4. 3% - Absorbed by _____________________ 5. 51% - Absorbed by ________________________________________. 6. 16% - Absorbed by _________________, water vapor and dust 100 Units of Insolation 1 6 2 4 5 3 Surface of Earth Re-radiation from Earth’s surface IV. Temperature & Heat A. Heat Transfer – how heat moves. 1. Conduction – Heat is transferred through the _________________________________________ a) This occurs best in _________________, where molecules are closely packed. Molecules vibrate _____________ when heat is applied. 2. _______________________ - Heat is transferred through the movement of ______________ & ____________________. a) As ___________ water rises it mixes with _________ water and creates an up and down pattern; called convection currents. 3. Radiation – Heat is transferred by __________________________________________ through air or space. a) __________________________, ____________________________ and other electromagnetic waves travel through a vacuum from the Sun to the Earth daily. Ex: ______________________________________________ Heat Transfer Factors that Affect the Amount/Rate of Heating 1. The ____________________ and ____________________________ of sunlight. a) ______________________/time of day (1) The angle of _____________________________________________________________ in the course of one day/seasons; ____________________________ intensity occurs at __________________/summer. Angle of Insolation Intensity of Insolation B. 9am (sunrise) 2. noon 9pm (sunset) Specific Heat - The ____________________________________________ per unit mass required _____________________________________________________________________ by one degree Celsius. 1. page _________ ESRT’s 3. _____________________ vs. _____________________ a) 4. Color: ___________________________________________________________ a) 5. __________________ heats up and cools down ___________________than water. _________________ colors heat up ______________________ than lighter colors. Texture: _______________________ vs. ________________________ a) _____________________ surfaces heat up _____________________ than smooth surfaces because rough surfaces have more surface area. C. Measuring Temperature – page _______ of ESRT V. Moisture – dampness that can be felt as vapor (gas) in the atmosphere or condensed liquid on the surfaces of objects. A. The Water Cycle 1. The primary source of _______________________ for the water cycle is the sun. 2. Transpiration is the process by which ____________________ release __________________ into the atmosphere. 3. ____________________________________ is falling liquid or solid water from the clouds to the Earth’s surface. a) B. Ex: ___________________________________________________________________________ Changes in States of Matter – page _______ of ESRT 1. States of Matter a) _____________________________ b) _____________________________ c) _____________________________ 2. Phases of Matter – how they _________________________ a) Evaporation ___________________________________________ b) ______________________________ Freezing c) _____________________________________ Deposition *Each of these paired phase changes occurs at the ______________ temperature, depending on the material. 3. _______________________ a) ______________________ _____________________________: occurs as a solid turns into a liquid; by warming. (1) Water must _________________________ 334 calories of _______________/heat to change 1g of ice into liquid water. b) _______________________________: occurs as a liquid turns into a solid; by cooling. (1) Water molecules ________________________________ the same amount of ___________________________ that is gained during melting. 4. _________________________________ a) ________________________________________: occurs as a liquid changes into a _________ (1) b) _____________________________ Water must _________________ 2260 calories of energy to change 1g of liquid water into water vapor. __________________________________________: occurs as a gas changes into a liquid (1) Water molecules ___________________________the same amount of energy that is gained during evaporation. (2) Condensation in the atmosphere results in the formation of _________________________ and _________________________________________. Calories/oC 5. Factors Affecting the Rate of Vaporization (Evaporation) a) R of V Temperature: As ________________________________ ______________________________ the rate of _____________________________________ ______________________________. b) Humidity: As ________________________________ _________________________________ the rate of ___________________________________ _________________________________. c) Wind: As __________________________________ ___________________________________ the rate of ________________________________________ ________________________________. d) R of V Surface Area: As _____________________________ area __________________________________ the rate of _________________________________ ________________________________________ e) Specific Heat: As ___________________________heat _______________________________ the rate of _________________________________________ __________________________________ R of V 6. R of V ___________________ a) _____________________ ___________________________________: occurs as a solid changes directly into a gas. (1) b) R of V Ex: Mothballs and ______________________________ ___________________________________: occurs as a gas changes directly into a solid. C. Moisture in the Atmosphere - the primary source for water in the atmosphere is the oceans. Other sources include ________________________________________________ 1. 2. Water exists as all three states in the atmospherea) Solid- minute ____________________________ suspended in the air b) Liquid- minute water ____________________________ suspended in the air c) Gas- ____________________________________ __________________________________ is the general term used to describe the ______________________ of water ______________________ in the air. 3. _________________________________ determines the amount of water vapor the air can ___________________. a) As air temperature ___________________________, the amount of water vapor the air can hold also increases. 4. __________________________________ occurs when air holds ______________________________ water vapor _______________________________ at a given ____________________________________. a) Rate of __________________________________ = Rate of _________________________________ A B C Saturated Unsaturated Unsaturated _________________________ ____________________________ air molecule water molecule ___________________________ Evaporation Condensation 5. Dew Point Temperature – the temperature to which ________________________________ __________________________________ to reach saturation. a) Measuring with a _____________________________________________________ (1) Two thermometers; one ______________ bulb and one _____________ bulb. (2) When whirled in the air evaporation occurs on the _____________ bulb. This causes the temperature of the wet bulb to _______________. (3) _________________________________ between the dry bulb and the wet bulb _____________________________________ the _____________________________ and the relative humidity of the air. (a) The air is saturated when the difference between the two bulbs equals ______________. (i) Dry air: greater difference between wet and dry bulbs. More _______________________ and cooling. (ii) Humid air: smaller difference between the wet and dry bulb. ________ evaporation and cooling. b) Measuring Dew Point: Use page _______ in your ESRT’s to complete the following table. Dry Bulb Temp 22oC 22 oC 20 oC 15 oC 9 oC 8 oC 17 oC Wet Bulb Temp 20 oC 13 oC 14 oC 12 oC 3 oC 6 oC 17 oC Difference Dew Point 6. ____________________________________________ - The ratio between the _____________________ amount of water ____________________ in the air to the _________________________ amount of water vapor the air can ___________________ at ant given temperature. 40o 20o 10o 1:2 1:1 1:4 Temperature a) Factors that affect Relative Humidity: (1) If the temperature _________________________________; and the amount of ____________________________________ remains the same, relative humidity will ___________________________________. (2) Time of day (a) ______________________ RH occurs around 5 am when it’s the ___________________________________ (b) ___________________________ RH occurs around 3 pm when air temperature is the _______________________________. b) Absolute Humidity: the ______________________________ amount of water vapor in the air. (1) If ______________________________ in the air increases and ____________________ remains the same, relative humidity will _______________________________. 1:4 2:4 Water Vapor 4:4 c) Measuring Relative Humidity: Use page _______ of the ESRT to complete the following chart. Dry Bulb Temp 20oC 8oC 22oC 22oC 15oC 15oC 3oC Wet Bulb Temp 14oC 6oC 13oC 20oC 12oC 15oC -1oC Difference Relative Humidity 7. Clouds – tiny droplets of __________________ water or minute ____________ crystals suspended in the air. a) Conditions needed for Cloud formation (1) __________________________________ in the air. (2) __________________________________ temperatures (3) Condensation _________________________________________ (a) b) Aerosols in the atmosphere; which provide a surface for liquid water/ice to condense upon. Precipitation ___________________________________________________________________________ c) Adiabatic Cooling: cooling in the atmosphere (1) As a parcel of __________________________________________, the amount of air _________________________ surrounding the parcel ___________________________. (2) The parcel will begin to _________________________ in volume as it rises. As it expands, it becomes __________________________. (3) When its temperature __________________ to its _____________________________ temperature, the water ____________________ in the air _____________________________________ and cloud forms in the sky. d) Cloud Types (1) __________________________________: wispy and light. (2) ___________________________________: Spread out or layered. (3) ___________________________________: Heaps or piles, vertical growth. (4) ___________________________________: Prefix meaning “high” (5) ___________________________________: Rain-bearing or snow-bearing e) Using the descriptions draw and label different cloud types below: VI. Air Pressure – The force of _______________________ causes the air to have _________________________; this creates air pressure. A. Air pressure acts ___________________________ in all directions 1. All objects that contain air have _____________________________________. a) B. Measuring air pressure: 1. Air pressure at sea level is ___________ pounds per square inch. 2. Standard atmospheric pressure at _______________________________ is: 3. C. Ex: ___________________________________________________________________ a) ______________________________________________________ b) ______________________________________________________ c) ______________________________________________________ Use page ________ in ESRT’s to convert millibars into inches of Mercury. a) 997 mb = ________________ in b) _________________ = 30.15 in c) 982 mb = _________________ in d) __________________ = 29.53 in _______________________ ________________________ _______________________ _________________________ Factors that cause a change in air pressure: 1. Temperature- as ____________ temperature ___________________________ molecules Pressure move _____________________________; and the air becomes less __________________________,) air pressure __________________________. Temperature Pressure 2. Moisture- as _____________________________ of the air _____________________________ air pressure ___________________________________. a) Moist/______________________ air holds more water __________________ molecules. b) Water vapor molecules are ____________________________ then the ______________ dry air molecules they replace. c) Humidity 3. Water vapor molecules replace dry air molecules during ________________ Altitude – as altitude ___________________________, air pressure _________________________. a) At __________________________ altitudes there is less air above you and the air is less __________________. VII. Wind – The _________________________ movement of air; ____________________ to Earth’s surface. A. Causes of Wind – 1. 2. B. ___________________________ heating of Earth’s surface. a) Land vs. _____________________ b) _____________________ vs. Equator c) Dark forest vs. ______________________________ Winds help distribute _______________________ from regions with ___________________ energy to regions with _________________ energy. Sea-Breeze vs. Land-Breeze 1. Sea-Breeze: a) Land air is warmer and _______________________________; ______________ pressure b) Air over Lake Ontario is cooler and _____________________________;____________ pressure. L H 2. Land-Breeze: a) Land air is cooler and more ____________________________; _______________ pressure. b) Air over Lake Ontario is warmer and ____________________ dense; ________________ pressure. L H C. Wind Direction – Winds always blow from regions of ______________ pressure to regions of ____________ pressure. 1. The Coriolis Effect: a) b) 2. The Earth’s __________________________ on it’s axis causes winds to be deflected. (1) Northern Hemisphere – to the ____________ ( _____________________________) (2) Southern Hemisphere – to the ____________ (_____________________________) Global Winds – cause by unequal distribution of insolation. Cyclones vs. Anticyclones: a) Anticyclones – ________________ pressure systems (1) Winds move in a ____________________________, _______________________ spiral. H Map view b) Cyclones – ________________ pressure system (1) Winds move in a _________________________________, ___________________ spiral. L Map view c) D. Side view of cyclone and anticyclone Wind Speed – the speed of the wind is determined by the difference in _______________________ between two locations. 1. Pressure ____________________________: The difference in air pressure at two separate locations. a) As the air pressure gradient _______________________________, wind speed ___________________. 2. Wind speed is measured in __________________________. a) _____________ knot = ____________ _______/________ Determining Pressure Gradient: ESRT (1) (2) 1. Where is the pressure gradient the greatest? _______________________ (3) 2. Where is the wind speed the slowest? (4) 3. What is the pressure gradient between Niagara Falls and Rochester? ______________________________ ______________________________ o Page __________ of ESRT’s VIII. Air Mass - A large body of ___________ in the ___________________________ with similar characteristics. Ex: _____________________________________________________ A. Source Region – a geographic region where air mass was _______________________ 1. B. Picks up ____________________________________________________________ that it formed over. Types of Air Masses – 1. Tropical – originates over ____________________ regions. a) 2. Polar – originates over ____________________________ regions. a) 3. ______________________________ Maritime – originates over _____________________________. a) C. Very ___________________ and ____________________/moist. Continental – originates over ____________________________________. a) 6. Very _________________ and ______________/ arid. Equatorial – originates over ____________________________ regions. a) 5. _______________________ temperatures Arctic - originates over _____________________________ regions. a) 4. ___________________ temperatures __________________/ humid. _______________________________ are a combination of _____________________________ and _________________________ conditions from their source region. Symbol Source Region Name of Air Mass Characteristics Continental Polar Cold & Dry mT Warm & Moist Continental Tropical cA Warm & Dry Very Cold & Very Dry Maritime Polar Cold & Moist D. USA – Source Regions IX. Weather Fronts - a _________________________ between __________________________________. A. Cold front – the front edge of a cold air mass _________________________________ and _________________________________ warmer air. 1. Narrow band of ___________________________________ usually comes before a cold front moves in. B. Warm- front – the front edge of a warm air mass ______________________________ and _____________________________ colder air. 1. A wide band of ______________________________________ usually comes just before a warm front moves in. C. Stationary front - _________ different air masses move ______________________ to each other and Earth’s surface. D. Occluded Front - two or ____________ air masses interact and combine at their ______________________________. E. Page ___________ of ESRT’s Today’s Weather Weather Report X. Weather Maps: A. Isoline – 1. A line connecting points of ________________________ on a map. a) B. Isotherm – 1. Lines that connect points of equal ____________________ a) C. Isolines illustrate weather _________________ on a map field. Points of equal value connect _________________ across the US.. Isobars – 1. Lines that connect points of equal ________________________ a) Points of equal value connect in _______________ on a map. D. Mapping a temperature field – 1. Connect points of equal temperatures in intervals of 10oF a) 30 (… 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80…) Calvary 27 50 Winnipeg Bismarck 40 34 33 Montreal 30 Butte 49 34 40 Boise 39 Minneapolis 40 42 44 57 Salt Lake City 60 San Francisco 46 New York City 40 Chicago 51 60 Denver Cincinnati 50 Kansas City 45 Richmond 63 68 62 Los Angeles Boston Buffalo Detroit 58 30 Farther Point 40 Seattle 3 0 70 68 54 57 Phoenix Roswell Chattanooga 56 Oklahoma City 71 Little Rock 71 Atlanta 58 Charleston 72 Fort Worth 60 Galveston Hatteras Jacksonville 76 New Orleans 77 Tampa 80 Miami 2. The greatest temperature gradient is between ______________________________ and __________________. a) 3. This is indicated by the isotherms being _________________________________________ Calculate the temperature gradient from Cincinnati to Chicago: a) Change in field value ÷ Distance = Gradient E. Mapping an air pressure field – 1. 2. Isobars are drawn in intervals of ____________ in the US. a) Decode station model pressure readings by adding a 9 or a 10 to the front of the number and a decimal between the last two digits. b) 040 = __________________, 120 = ____________________, 759 = _________________ Connect points of equal air pressure in intervals of 4 mb. Identify areas of high or low pressure by labeling the middle with an H/L XI. Weather Trends/_______________________: A. Weather systems move ________________ to _______________ across the USA. 1. This trend is caused by the __________________________________________; due to Earth’s rotation from _________________ to __________________. B. Regent’s Maps - contain ___________________ models and/or ________________. C. Extreme Weather: 1. Hurricanes – a) _________ pressure; storm systems b) Fueled by energy _____________________________ over ________________ ocean water. (1) 2. Fueling is caused by ___________________________________. c) _________________________________ energy over land; loses fuel source. d) Extremely high ________________; blowing _______________. Tornadoes – a) A violently rotating ________________________ of air, in contact with the ground. b) Stems from a ________________________ cloud or just underneath a cumulus cloud. c) Often visible as a _______________________ cloud. d) Cause: (1) _______________ air moves over _________________ air. (2) During developing _______________________________________ (3) Typically in the ___________________________________