* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Adding and Subtracting mixed numbers
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Vincent's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Elementary arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Collatz conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
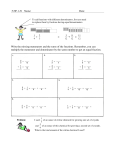
Math – Study Guide Chapter 4 (4.1 ~ 4.2) Topics to be included: 1)Writing Fractions as Decimals Two different ways: a) Division ~ always works! 3 4 5 9 2 .75 .55555 = .5 4 | 3.00 9 | 5.00 - 28 - 45 20 50 -20 0 b) If the denominator is a factor of 10, 100, 1000 multiply numerator and denominator by that number ~ simplify 6 12 = (x 2) = .12 100 50 2) Writing Fractions as Decimals Say the name of fraction ~ divide by the place value ~ simplify 0.02 = two hundredths = 2 1 = 100 50 3) Comparing Rational Numbers Compare fractions ~ Make denominators same ~ Compare numerators OR Cross multiply fractions Example: Compare - 1 3 □ 4 8 Cross Multiply □ -1 4 -3 8 so – 1 3 >4 8 Compare decimals ~ Compare every digit Example: Compare 0.25 □ .27 Tenths -> both 2 Hundredths -> 5 < 7 So, 0.25 < 0.27 4) Ordering Rational Numbers Change all fractions into decimals, compare and order. Example: Order from least to greatest: 0.056, 1 5 , -0.2, 20 9 Convert the fractions into decimals. 0.056 0.05 ( 1 ) 20 In order from least to greatest: 5 1 -0.555 (- ), -0.2, 0.05 ( ), 0.056 9 20 -0.2 5 -0.5 (- ) 9 Math – Study Guide Chapter 4 (4.3 ~ 4.5) Topics to be included: 1) Adding Like & Unlike Fractions Same Denominators Different Denominators 2/5 + 3/5 5/5 = 1 2/7 mult by 5 + 3/5 mult by 7 10/35 + 21/35 31/35 2) Subtracting Like & Unlike Fractions Same Denominators - Different Denominators 4/5 3/5 1/5 - 5/6 mult by 1 2/3 mult by 2 5/6 - 4/6 1/6 3) Adding/Subtracting Mixed Numbers Same Denominators Different Denominators 3 2/7 + 2 3/7 5 5/7 9 7/10 mult by 1 - 4 3/5 mult by 2 9 7/10 - 4 6/10 5 1/10 Different Denominators & Borrowing 4 1/3 mult by 5 - 3 3/5 mult by 3 4 5/15 - 3 9/15 * Cannot perform 5 -9, so borrow 1) Subtract whole number by 1: 4-1 = 3 2) Add denominator to numerator and make that your new numerator: 5 + 15 = 20 3) Subtract whole numbers 3 20/15 - 3 9/15 11/15 Subtracting from a whole number 1) Subtract whole number by 1: 12 – 1 = 11 2) Make a fraction have the same numerator and denominator as the second fraction: 4/4 3) Subtract whole numbers 12 - 3 1/4 11 4/4 - 3¼ 8 3/4 Math – Study Guide Chapter 4 (4.6, 4.8) Multiplying Fractions 1. 2. 3. 4. Make into improper Cross Simplify Multiply across Simplify (if needed.) Examples: 5 4 5 2 1 · = · = 8 10 8 5 4 2 ∙ 7 8 = 2 7 ∙ = 1 8 14 6 3 =1 =1 8 8 4 - 2 15 5 15 ∙ ∙ =5 22 8 88 2 2 8 12 32 ∙ 12 = ∙ = = 32 3 3 1 1 Dividing Fractions 1. 2. 3. 4. Change mixed numbers into improper fractions Keep the first fraction. Change the division sign to a multiplication sign Flip the second one (the divisor) upside down *** Remember this is called the reciprocal *** 5. Follow the multiplication rules. Examples: 4 8 4 9 3 ÷ = · = 6 9 6 8 4 10 1 3 21 7 21 4 6 ÷1 = ÷ = ∙ = =6 2 4 4 2 2 7 1