* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA Model Activity
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
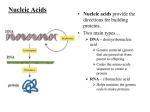
Name: _____________________________ DNA Model Activity What is the structure of DNA? Background Information DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is found in the chromosomes of all living things. It is the chemical of which genes are composed. With an understanding of this all-important molecule, scientists know how chromosomes can duplicate during cell division and transfer genetic information to new cells. They also understand the functioning of DNA instructions sent out to direct the activity of protein formation within the cell. The DNA molecule is in the shape of a DOUBLE HELIX (spiral). The molecules making up the DNA molecule are DEOXYRIBOSE SUGAR, PHOSPHATE GROUP, and NITROGEN BASES. A molecule of deoxyribose sugar bonds with a phosphate group with a strong PHOSPHODIESTER BOND. The deoxyribose, phosphate and a nitrogen base together form the structural unit of DNA called a NUCLEOTIDE. There are four different nitrogen bases available to form nucleotides. The nitrogen bases are ADENINE, GUANING, THYMINE, and CYTOSINE. Adenine and guanine are larger molecules and are called purines. Thymine and cytosine are smaller molecules and are called pyrimidines. In this activity, you will work with hour lab partner to construct a model of DNA using paper cutouts, colored pencils, and tape. Procedure 1. Fill in the following key with the colors you will use in your DNA model. Be sure to choose a different color for each component of the DNA molecule. Structural component of DNA Phosphate Deoxyribose Sugar Adenine Guanine Thymine Cytosine Color 2. Color the pieces on the DNA structure sheets according to the table you filled out above. You will need to color: 6 Adenine 6 Cytosine 6 Guanine 6 Thymine 24 Deoxyribose 24 Phosphates 3. Once you have finished coloring all of the pieces, cut them out so you will be able to assemble the nucleotides that will build your DNA molecule. 4. Create one of each of the different nucleotides that will build your DNA molecule. Show these nucleotides to your teacher for approval BEFORE you assemble your DNA molecule. Teacher: ________ 5. Use the following sequence of nitrogen bases when assembling your molecule of DNA. T A C G T A C A T G C G (right strand) What will the complementary strand look like ? __________________________________ (left strand) 6. Create the strands of DNA by taping the nucleotides in the appropriate order. It is helpful if one partner is responsible for creating the right strand of the DNA molecule and the other partner creates the left strand. 7. Once both partners have each side of the DNA correctly assembled, connect the two strands together. REMEMBER: Adenine ALWAYS joins with _________________ Guanine ALWAYS joins with _________________ Analysis Questions: 1. What two chemicals make up the sides of the DNA molecule? 2. What chemicals make up the “rungs” (steps) of the DNA ladder? 3. What makes Adenine and Guanine similar? 4. What makes Cytosine and Thymine similar? 5. What type of bond holds the nitrogen bases together? 6. What are the parts of a nucleotide? 7. How many different nucleotides are possible in any DNA molecule? 8. How does the location of DNA differ between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? 9. How does the structure of DNA differ between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? 10. What is the name that is used to describe the three dimensional shape of DNA? 11. If four GUANINE nucleotides are found in a DNA segment, how many CYTOSINE will be found in the same DNA segment? Explain your answer! 12. The following represents the nitrogen bases found on a DNA molecule. In the spaces provided, name the complementary nitrogen bases that would pair with the bases provided. THYMINE ________________ ADENINE ________________ GUANINE ________________ ______________ CYTOSINE ______________ THYMINE CYTOSINE _________________ _______________ THYMINE ADENINE _________________ CYTOSINE _________________ _______________ ADENINE _______________ GUANINE