* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Dynamic Earth Ch. 3 Sect. 1 Objectives Describe the
Survey
Document related concepts
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
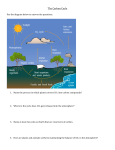
The Dynamic Earth Ch. 3 Sect. 1 Objectives Describe the composition and structure of the Earth. Describe the Earth’s tectonic plates. Explain the main cause of earthquakes and their effects. Identify the relationship between volcanic eruptions and climate change. Describe how wind and water alter the Earth’s surface. Earths Layers __________________(rock), __________________ (air), _________________ (water) __________________ (living things) The Earth Below Us The Crust (dense) ______________________________ Only 1% of Earth’s mass ______________________________ The Mantle (denser) 64% of Earth’s mass ______________________________ The Core (most dense) ______________________________ Plate Tectonics Lithosphere – Earth’s outer most layer and ____________________________ Asthenosphere – layer directly below the lithosphere, ___________________ Tectonic Plates are in the lithosphere and move because of the moving rocks in the asthenosphere There is a lot of activity at the boundaries of tectonic plates Colliding – ______________________________ Sliding – ______________________________ Moving away – ______________________________ This causes many natural phenomena to occur Mountains (colliding) Earthquakes (slipping or sliding) Volcanoes (colliding or separating) Mountains Made by plates: ______________________________ Example: Himalaya Mountains - Eurasian Plate and Indian Plate collided Earthquakes Fault – _____________________________________________________________ (tectonic plate boundaries) Causes Tectonic plates slipping, causes vibrations Magnitude – ______________________________ Volcanoes - ______________________________ Magma - melted rock that rises from the interior of the earth to the surface Global effects: ______________________________ Reduce the amount of sunlight reaching earth ______________________________ Erosion - __________________________________________ Wears down rocks and makes them smoother Rocky Mountains vs. Appalachian Mountains Sect. 2 Objectives Describe the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere. Describe the layers of the Earth’s atmosphere. Explain three mechanisms of heat transfer in Earth’s atmosphere. Explain the greenhouse effect. Atmosphere - ______________________________ Nitrogen – 78% Oxygen - 21% Carbon Dioxide, argon, methane, water vapor – 1% Aerosols - ____________________________________________________ Atmospheric Layers Troposphere ______________________________ Almost all weather occurs here ______________________________ Temperature decreases as Altitude increases Stratosphere Above the Troposphere _____________________________ Includes the Ozone layer -Reduces UV radiation that reaches the Earth Mesosphere Above the Stratosphere ______________________________ Thermosphere ______________________________ Hottest layer! Because Nitrogen and Oxygen absorb solar radiation. Over 2000oC Would not feel hot to us. Why? ______________________________ Energy In the Atmosphere Radiation – ______________________________ Ex: Energy from the sun Convection – ______________________________ Ex: wind Conduction – _____________________________ Greenhouse Effect 1.Sunlight enters Earth’s atmosphere 2.Earth’s surface radiates heat back to the atmosphere Some heat escapes Some heat is trapped by Greenhouse Gases Ex: water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide 3.Trapped heat radiated back to Earth’s surface, warming the air. Without this Earth would be too cold to live on However, too many greenhouse gases can trap too much heat. Sect. 3 Objectives Name the three major processes in the water cycle. Describe the properties of ocean water. Describe the two types of ocean currents. Explain how the ocean regulates Earth’s temperature. Discuss the factors that confine life to the biosphere. Explain the difference between open and closed systems. Water Cycle - ______________________________ Evaporation – water heated by the sun rises into the atmosphere Condensation – water in the atmosphere cools and forms water droplets on dust particles Precipitation – ______________________________ Snow, sleet, hail, rain Transpiration – ______________________________ Rock Cycle – draw in your EcoLog!! World Ocean - ____________________________________________________ Pacific Ocean – Largest Contains the deepest part of the ocean – Challenger Deep at the bottom of the Mariana Trench Atlantic Ocean Indian Ocean Arctic Ocean – smallest ______________________________ The World Temperature Regulator The Oceans!!!! Absorbs and stores energy from the sun, this helps regulate the temperature on Earth. Releases heat slowly when it is cold Absorbs heat when it is hot Milder temperatures occur by large bodies of water Can regulate the temperature in areas Ex: The Gulf Stream affects the British Isle climate