* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download right ventricle
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
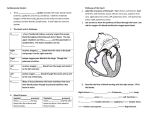
Blood Flow: Human Heart arch of aorta superior vena cava (from head, upper limbs) trunk of pulmonary arteries right semilunar valve (shown closed); to the pulmonary trunk left semilunar valve (shown closed); to aorta right pulmonary veins (from lungs) left pulmonary veins (from lungs) right atrium left atrium right AV valve (shown open) left AV valve (shown open) right ventricle left ventricle (muscles that prevent valve from everting) endothelium and underlying connective tissue inferior vena cava (from trunk, legs) septum (partition between heart's two halves) inner layer of pericardium myocardium heart’s apex Fig. 33-11c, p.560 Circuits • Systemic (transport of: O2, CO2, nutrients, waste), left side • Pulmonary (respiratory interface: O2, CO2, exchange), right side – heart beats about 100,000 times every day or about 35 million beats per year Systemic Circuit Longer loop that carries blood to and from body tissues capillary beds of head and upper extremities (to pulmonary circuit) aorta (from pulmonary circuit) heart capillary beds of other organs in thoracic cavity capillary bed of liver capillary beds of intestines Pulmonary Circuit right pulmonary artery Short loop that oxygenates blood capillary bed of right lung left pulmonary artery capillary bed of left lung pulmonary trunk (to systemic circuit) (from systemic circuit) pulmonary veins heart lungs Direction of Blood Flow 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Superior and inferior vena cava Right atrium Right ventricle Pulmonary artery (Pulmonary circuit) Pulmonary veins (Pulmonary circuit) Left atrium Left ventricle Aorta Systemic Circuit (Arteries [elastic], Arterioles, Capillaries, Venules, Veins). Back to # 1 Figure 19.6 Cardiac Cycle • All events associated with one heartbeat • two atria contract – while two ventricles relax • two ventricles contract – while two atria relax Fluid pressure in filling atria opens AV valves; blood flows into ventricles. Ventricles relax even as the atria begin to fill and start another cycle. Atria contract, and fluid pressure in ventricles rises sharply. Ventricles contract; blood is pumped into the pulmonary artery and the aorta. Fig. 33-12, p.561 Summary Two simultaneous circuits: systemic and pulmonary Ventricles = muscular chambers of the heart that eject blood (aorta, pulmonary arteries) Atria = collecting chambers of the heart that contract to fill the ventricles • left side pumps to systemic circuit • right side pumps to pulmonary circuit