* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 21
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
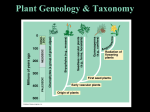
Ch. 21 What Is a Plant? 21.1 Adapting to Life on Land A. Origins of Plants – A plant is a ______________________________________________________ that can produce glucose (food) through photosynthesis. They contain cell walls made of _______________________. 1. _______________________ – a waxy waterproof coating of stems and leaves that prevents water loss B. Adaptations in Plants 1. Preventing water loss – Many land plants are covered with waxes and oils that prevent water loss 2. Leaves carry out photosynthesis a. __________________ – a broad, or flat structure of a plant that traps light energy for photosynthesis (contain chloroplasts) 3. Putting down roots a. ___________– a plant organ (“anchor”) that absorbs water and minerals from the soil and transports those nutrients to the stem (ex: some are food: carrots, radish…) 4. Transporting materials a. _________ – provides structural support for upright growth and contains tissues for transporting water and food b. ____________ ___________ - long, tubelike cells that transport water, food and minerals in “vascular plants” c. ____________ ___________ – do not have vascular tissue (ex: mosses, hornworts, and liverworts 5. Reproductive strategies – some plants reproduce with seeds. _______________________ use sperm that swim through water to get to the egg a. _______________________ – contains an embryo, along with a food supply, covered by a protective coat that protects the embryo 6. Alternation of Generations – the lives of all plants consist of two generations: _______________________ (N) and _______________________ (2N) 21.2 Survey of the Plant Kingdom A. Phylogeny of Plants – Biologists classify plants into 12 ____________________ (similar to phylums) B. Non-seed Plants – there are seven divisions of non-seed plants, 3 are non-vascular which rely on osmosis and diffusion for transporting water and nutrients. NON-SEED, NON-VASCULAR PLANTS 1. Division _________________ 2. Division _________________ 3. Division ____________ common name: liverworts – have common name: hornworts – common name: mosses – flattened bodies that look like an sporophytes resemble the horns of low growing plant. Nonanimal’s liver. Non-vascular. an animal. Non-vascular. vascular. NON-SEED, VASCULAR PLANTS 4. Division _________________ , 5. Division ________________ 6. Division ______________ common name: whisk ferns – common name: club mosses – ,common name: horsetails – Vascular plant with no roots or Vascular plant with stems roots Vascular plant with scalelike leaves and leaves. leaves. 7. Division _________________ , common name: ferns – Vascular plant mostly grown in tropics a. _________________ – in ferns, large, complex leaves that grow upward from the rhizome; often attached to pinnae that are attached to a central stipe. C. SEED, VASCULAR PLANTS 8. Division _________________ , common name: cycads – palmlike trees with scaly trunks. Produce male and female cones. a. _________________ – scaly structures that support male or female reproductive structures. Seeds are produced in female cones, male cones produce pollen. 9. Division _____________ 10. Division ______________ common name: climbing ___common name: ginkgo – vines only 1 species exists, has fanshaped leaves 12. Division _________________ common name: flowering plants – produce flowers and seeds enclosed in a fruit 11. Division _________________, common name: conifers (pine, fir, cypress, redwood…) – produce seeds in cones, contain needlelike leaves.