* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Geneology & Taxonomy
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
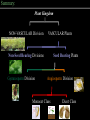
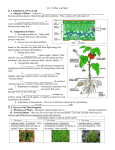
Plant Geneology & Taxonomy I. NON-VASCULAR PLANTS No special system of vessels to transport fluids internally. • Examples: mosses, liverworts II. VASCULAR PLANTS Special vessel-like system for transmission of fluids internally. A. Non-Seed Bearing Reproduce through spores • Examples: Horsetail, Ferns II. VASCULAR PLANTS B. Seed-bearing: 1. Gymnosperms – Leaves are needle-like or scaly – Do not produce flowers – Many produce cones to protect seeds - conifers – Seeds not enclosed in fruit – Stems are woody • Example: pines, redwood II. VASCULAR PLANTS B. Seed-bearing 2. Angiosperms – Leaves are flat – Produce flowers – Seeds are enclosed in fruits – Stems can be woody or non-woody – Divided into two groups: monocots & dicots II. VASCULAR PLANTS 2. Angiosperms a. Monocots – Flower parts in multiples of 3 – one cotyledon in seed – parallel leaf veins • Example: grasses, corn II. VASCULAR PLANTS: 2. Angiosperms: b. Dicots – Flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5 – two cotyledons – networked leaf veins • Example: most other species Summary: Plant Kingdom NON-VASCULAR Division VASCULAR Plants Non-Seed Bearing Divisions Gymnosperm Division Seed Bearing Plants Angiosperm Division Monocot Class Dicot Class Flowering plants Cone-bearing plants Ferns and their relatives Flowers; Seeds Enclosed in Fruit Mosses and their relatives Seeds Water-Conducting (Vascular) Tissue Green algae ancestor