* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download practice test2
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Properties of water wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Vapor-compression refrigeration wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Liquid–liquid extraction wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Diamond anvil cell wikipedia , lookup
Glass transition wikipedia , lookup
Separator (oil production) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic reforming wikipedia , lookup
Countercurrent exchange wikipedia , lookup
Solid nitrogen wikipedia , lookup
Crystallization wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Equilibrium chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Vapor–liquid equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
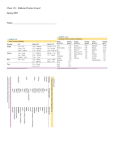
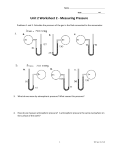
Chem 121: Midterm Practice Exam2 Spring 2009 Name:_______________________________________ PV=nRT R=0.0821 L·atm/mol·K Energy = SH x Mass x ΔT SHH20 = 1 cal/g°C For Water: HFusion = 80. cal/g Hvap = 540 cal/g @STP 1 mol gas = 22.4L 1atm = 760 mmHg = 101.3kPa M1V1=M2V2 Multiple Choice (1 pt each) 1) Which of the following is an example of potential energy? A) B) C) D) 2) In which of the following would the particles move slowest? A) B) C) D) E) 3) Water above its boiling point Liquid Water Water at its freezing point Water below its freezing point They all move at the same speed The physical state(s) present when a substance is melting is (are) A) B) C) D) E) 4) Running Water A skier at the bottom of the slope A car driving A skier waiting at the top of the slope Gas Gas + Liquid Liquid Liquid + Solid Solid Which of the following does NOT represent a step on the heating curve of water? A) The temperature of steam cannot exceed 100°C. B) The temperature of ice remains at 0°C as it melts. C) The temperature of liquid water increases linearly as it is heated D) The temperature of liquid water remains at 100°C as it boils E) Both liquid water and ice are present at 0°C. 5) Which measurement describes the Temperature of a gas? A) 315 K B) 1.2 g/L C) 2.5 L D) 725 mmHg. E) 0.45 moles 6) At STP conditions, 11 g of SO2 have a volume of A) 2.6 L B) 3.8 L C) 77 L D) 0.0038 L E) 120 L 7) As you rise higher in Earth's atmosphere, the atmospheric pressure A) Increases B) Decreases C) Stays the same 8) The atmospheric pressure on a certain day is 749 mm Hg, what is the partial pressure of nitrogen, given that nitrogen is about 78% of the atmosphere? A) 810 mmHg B) 584 mmHg C) 78.0 mmHg D) 165 mmHg E) 749 mmHg 9) In a solution, the solvent A) is a liquid B) can be a liquid or gas C) can be a solid, liquid, or gas. D) is never a solid E) is the substance present in the smallest concentration 10) Which of the following molecules can form hydrogen bonds A) CH4 B) NaH C) NH3 D) BH3 11) In water, a substance that ionizes completely in solution is called a A) Weak electrolyte. B) nonelectrolyte. C) semiconductor. D) strong electrolyte. E) nonconductor. 12) The name of Al2(SO4)3 is A) aluminum(III) sulfate. B) dialuminum trisulfate. C) dialuminum sulfate. D) dialuminum trisulfide. E) aluminum sulfate. 13) When some of the sugar added to iced tea remains undissolved at the bottom of the glass, the solution is A) dilute B) unsaturated C) saturated D) polar 14) A catalyst is A) a reactant in a chemical reaction B) a product in a chemical reaction C) a substance that speeds up a reaction without being consumed in the reaction D) a substance that increases the energy of the products 15) What is the correct form of the equilibrium constant for the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen to form water? The equation is: 2H2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ H2O(g) A) Kc = B) Kc = . C) Kc = D) Kc = . Chapter 6: For the reaction: 2H2O(l) + 137 kcal → 2H2 (g) + O2 (g) How many kcal are needed to form 2.00 moles O2 (g)? Is this reaction endothermic or exothermic? The melting point of benzene is 5.5ºC and its boiling point is 80.1ºC. Sketch a cooling curve for benzene from 100ºC to 0ºC. Chapter 7: A steel cylinder with a volume of 12.0L is filled with 30.0g nitrogen gas at 1 atm. What is the Temperature of the gas in the cylinder? A balloon has a volume of 250 L when filled with helium at 12ºC at a pressure of 300 mmHg. What is the new volume of the balloon when the pressure is 1.00 atm and the temperature is -25ºC? What is the total pressure in mmHg of a gas mixture containing Argon at 1.2 atm, Helium at 3250 mmHg, and Nitrogen at 230 mmHg? Chapter 8: How many grams of HCl are in 34.8 mL of a 10.0 M HCl solution? What is the molarity when 0.5 L of 12M NaOH is diluted to a final volume of 2 L? A solution of NaCl is added to a solution of AgNO3 and a precipitate forms: NaCl + AgNO3 NaNO3 + AgCl Write down the Net Ionic equation and state which compound is the precipitate (AgCl) If 500. mL of a 1.5 M NaCl solution was added to excess AgNO3 solution, how many grams of AgCl would form? Chapter 9: Consider the reaction: Heat + PCl5 (g) ⇌ PCl3 (g)+ Cl2 (g) What is the correct form of the equilibrium constant (Kc) for this reaction? At 400 K the Equilibrium constant (Kc) is 3.75, the concentration of PCl5 is 1.2M, the concentration of Cl2 is 2.5M, what is the concentration of PCl3? Will the following changes to the system increase or decrease the concentration of the products? -Adding more PCl5 -Increasing the Temperature -Increasing the Pressure