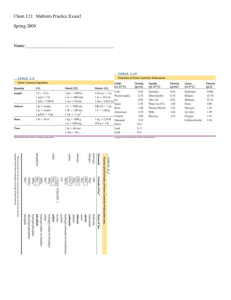
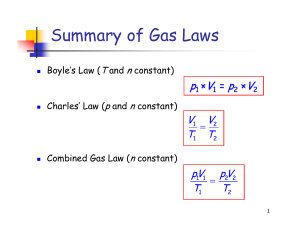
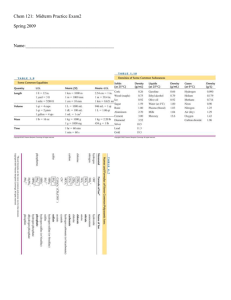
9/21 properties of matter ppt
... distilled first. This liquid turns into a vapor (gas) and flows out the distillation flask. As it enters the condensing tube, it is cooled and condenses back into a liquid. It is then collected in a graduated cylinder. When the liquid is almost completely evaporated the liquid with the next lowest b ...
... distilled first. This liquid turns into a vapor (gas) and flows out the distillation flask. As it enters the condensing tube, it is cooled and condenses back into a liquid. It is then collected in a graduated cylinder. When the liquid is almost completely evaporated the liquid with the next lowest b ...
practice test2(Answers)
... A) The temperature of steam cannot exceed 100°C. B) The temperature of ice remains at 0°C as it melts. C) The temperature of liquid water increases linearly as it is heated D) The temperature of liquid water remains at 100°C as it boils E) Both liquid water and ice are present at 0°C. ...
... A) The temperature of steam cannot exceed 100°C. B) The temperature of ice remains at 0°C as it melts. C) The temperature of liquid water increases linearly as it is heated D) The temperature of liquid water remains at 100°C as it boils E) Both liquid water and ice are present at 0°C. ...
practice test2
... Which of the following molecules can form hydrogen bonds A) CH4 B) NaH C) NH3 D) BH3 ...
... Which of the following molecules can form hydrogen bonds A) CH4 B) NaH C) NH3 D) BH3 ...