* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Download country indicators
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Views on the Kyoto Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Decarbonisation measures in proposed UK electricity market reform wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Energiewende in Germany wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Carbon governance in England wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Canada wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Business action on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
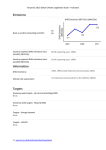
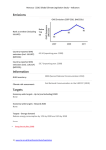
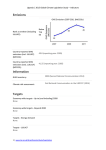
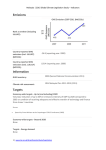
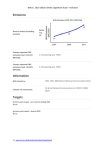
Japan | 2015 Global Climate Legislation Study – Indicators Emissions GHG Emissions 2007-2011 (MtCO2e) Rank as emitter (including LULUCF): 610 Country-reported GHG emissions (incl. LULUCF) (MTCO2): 1268.05 (reporting year: 2012) Country-reported GHG emissions (excl. LULUCF) (MTCO2): 1343.12 (reporting year: 2012) Information GHG inventory: 1990-2012 (GHG inventory submission of 2014) Climate risk assessment: Comprehensive Research on Impact Assessment and Adaptation for Climate Change (2014) Targets Economy wide targets - Up to (and including) 2020 3.8% reduction below the 2005 baseline by 2020 Source: Announcement at the Warsaw COP19 Conference (2013) Economy-wide targets - Beyond 2020 80% reduction of GHG emissions by 2050 Source: The Fourth Basic Environment Plan (2012) 1 | www.lse.ac.uk/GranthamInstitute/Legislation Japan | 2015 Global Climate Legislation Study – Indicators Targets - Energy demand None Targets - LULUCF None Targets - Renewables None Targets- Transport Increase the share of highly energy-efficient next-generation vehicles in the new car sales from 50% to 70% by 2030 Source: 6th communication to the UNFCCC (2013) Policies GHG Mitigation framework Law Concerning the Promotion of the Measures to Cope with Global Warming (Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures) (1998) Source: Law Concerning the Promotion of the Measures to Cope with Global Warming (Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures) (Law No. 107 of 1998), (1998) Adaptation framework None Policies - Carbon pricing Carbon tax for climate change mitigation purpose (began October 2012); Voluntary Emission Trading Scheme (started 2005); Carbon offset credit system Japan-Verified Emission Reduction (J-VER, 2008) Source: Act Partially Amending the Law on Special Tax Measures (Tax Reform Act 2012) (Law No. 16 of 2012), (2012) 2 | www.lse.ac.uk/GranthamInstitute/Legislation Japan | 2015 Global Climate Legislation Study – Indicators Policies - Promotion of low-carbon energy (inc. renewables) Renewable sources electricity purchase obligation for utilities; Feed-in tariff for renewable energy Source: Act on Purchase of Renewable Energy Sourced Electricity by Electric Utilities (Law No. 108 of 2011), (2012) Policies - Energy demand Low Carbon City Development Plan (local governments, low carbon buildings certification, tax reductions for high energy efficiency buidlings); Promotion of Contracts Considering Reduction of Emissions of Greenhouse Gases (green contracts); Designated emitters (workplace with over 1,500kL of oil equivalent of energy annually) are mandated to develop a Plan for Global Warming Countermeasure and report emissions; Energy efficiency standards for appliances, energy conservation labelling; Top Runner Programme (certification) for energy-savings performance; Voluntary energy efficiency and conservation campaigns (MOEJ-led, COOL BIZ, WARM BIZ); Subsidy on interest payment (max 1% per year) for so-called Òeco-loanÓ businesses, which reduced the amount of CO2 emission by more than 5% within the 5 years Source: Low Carbon City Promotion Act (Eco-city Law) (Law No. 84 of 2014), (2012) Law Concerning the Promotion of Contracts Considering Reduction of Emissions of Greenhouse Gases and Others by the State and Other Entities (Environment Consideration Contract Law) (Law No. 56 of 2007), (2007) Law Concerning the Promotion of the Measures to Cope with Global Warming (Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures) (Law No. 107 of 1998), (1998) Law Concerning the Rational Use of Energy (Energy Conservation Act) (Law No.49 of 1979), (1979) Policies - Transport Energy efficiency standards for vehicles; Tax incentives for low-polluting and nextgeneration cars(green tax 2002, eco-car tax 2009) Source: Law Concerning the Rational Use of Energy (Energy Conservation Act) (Law No.49 of 1979), (1979) Act Partially Amending the Law on Special Tax Measures (Tax Reform Act 2012) (Law No. 16 of 2012), (2012) Policies - LULUCF None 3 | www.lse.ac.uk/GranthamInstitute/Legislation