* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Practice Exam 1.1
Survey
Document related concepts
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
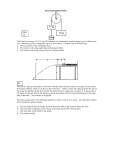
Practice Exam 1.1 Choose (i) four from problems 1 – 6 and (ii) three from problem 7! All problems are worth 20 points Problem 1 Two tiny conducting spheres carry charges of +3.0 μC and +2.0 μC. They are separated by a distance of 10 cm. a. Sketch a diagram of the E-field. b. What is the electric field (magnitude and direction) that each sphere experiences? c. What force will a proton (magnitude and direction) experience if placed there? Answer: 3.96×107 N/C, 6.34×10-12 N. Problem 2 In a television picture tube, electrons strike the screen after being accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 25 000 V from parallel plates. (a) Sketch a diagram of the electric potential the electrons see. Why are the electrons accelerated? (b) Find the electron speed just before the electron strikes the screen. [me = 9.11×10-31, e = 1.6×10-19 C] Answer: 9.4×107 m/s. Problem 3 a. A wire of Nichrome (a nickel–chromium–iron alloy commonly used in heating elements) is 1.0 m long and 5.64 mm radius. It carries a current of 4.0A when a 2.0V potential difference is applied between its ends. Calculate the resistivity of Nichrome. b. A circuit contains a 48-V battery and a single light bulb whose resistance is 240Ω. A second, identical, lightbulb can be wired either in series or in parallel with the first one. Determine the power delivered to a single bulb when the circuit contains (i) only one bulb, (ii) two bulbs in series, and (iii) two bulbs in parallel. Answer: 5.0×10-7 Ω∙m, 9.6W, 2.4W, 9.6W Problem 4 Find the (a) equivalent resistance of the circuit, (b) the voltage across and (c) the current through each resistor, and (d) the current coming from the battery for the circuit shown. Answer: (4V, 2A), (6V, 1.5A), (1V, 0.5A), (5V, 0.5A), 2A Problem 5 a. In a certain region, the earth’s magnetic field has a magnitude of 5.1 × 10-5 T and is directed north at an angle of 58o below the horizontal. An electrically charged bullet is fired north and 11o above the horizontal, with a speed of 670 m/s. The magnetic force on the bullet is 2.8 × 10-10 T directed due east. (i) Draw a diagram that shows v, B and FB. (ii) Determine the bullet’s electric charge, including its algebraic sign. Answer: −8.3 nC b. A particle of charge +7.3μC and mass 3.8 × 10-8 kg is traveling perpendicular to a 1.6-T magnetic field, as the drawing shows. The speed of the particle is 44 m/s. Determine the value the angle θ and ymax such that the particle’s subsequent path will intersect the y axis at the greatest possible value of y? Answer: 0.29m Problem 6 A wire loop with an area of 0.020 m2 is in a magnetic field of 0.30 T directed at a 30° angle to the plane of the loop. If the field drops to zero in 45 ms, what is the average induced emf in the loop? Answer: 0.11V Problem 7 Use short concise sentences to answer 3 of the 5 following questions using physics principles. Make sure to explain your reasoning for each answer. a. Your clothing tends to cling together after going through the dryer. Why? How does dryer (or antistatic cling) sheets help keep clothes from sticking together in the laundry dryer? b. A charge on the left moves from A to B, where at B the incoming charge comes to rest momentarily. (i) Explain why the electron comes to rest using (i) an electric field picture and (ii) using conservation of energy. c. (i) What is the role of the emf in a battery? (ii) Explain how the resistance depends on length, area, and material. d. You connect a number of identical light bulbs to a flashing battery. What happens to the brightness of each bulb as more and more bulbs are added to the circuit if you connect them in (i) series? (ii) parallel? Will the battery last longer if the bulbs are in series or in parallel? e. A loop of wire is horizontal. A bar magnet is pushed toward the loop from below, along the axis of the loop. (i) In what direction is the current in the loop? (ii) Is there a magnetic force on the loop? If so, in which direction? (iii) Is there a magnetic force on the magnet? If so, in which direction?