* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circuit_Electricity
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
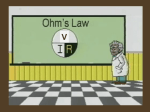
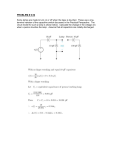
Circuit Electricity May 30, 2012 Chapter 22 Terms Current: Flow of charge Symbolized by “I” Units = Coulombs/second = Amperes (A) Circuit: a closed loop that current flows through Resistance: Opposition to current Units = Ohms (Ω) LED: Light Emitting Diode Used to test for presence of current. More Terms Volts: the force that pushes current through a circuit Power: the energy delivered to the circuit per second Power = (current)(voltage) P = (I)(V) Units = Watts Examples #1 & #2 A car battery causes a current of 2.0 amps through a light while 12 V is across the battery. What is the power used by the lamp? P = (2.0)(12) P = 24 W What is the current through a 75W lightbulb connected to a 120 V outlet? 75 = (I)(120) I = .625 A How does a light bulb light? As the current flows through the filament, it encounters resistance Resistance: a material’s opposition to current flow Ohm’s Law: R = (V/I) As resistance increases, current decreases As voltage increases, current increases The collisions between the current and material results in energy loss (heat and light) Examples #3 & #4 A car headlight has a resistance of 30Ω and is hooked to a 12V battery. What is the current through the bulb? 30 = (12/I) I = (12/30) = .40 A A lamp draws a current of .50A when connected to a 120-V outlet. What is the resistance of the lamp? R = (120/.50) R = 240 Ω Homework Ch 22 p 527-529 # 22,23,25,27,30,33,42,45