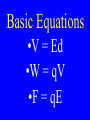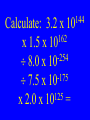* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Psc CH-21 Electric Fields
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
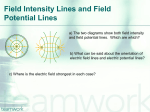
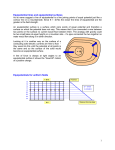
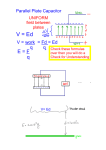
An electric force of -5 4.5 x 10 N is measured between two particles. One particle has a charge of -6 2.0 x 10 C & the other has a -8 charge of 3.0 x 10 C. Calculate the distance between them. Chapter 21 Electric Fields Electric force like gravitational force is inversely proportioned to the square of the distance between the two points of concern Electric Field (E) •A vector quantity that relates the force exerted on a charge to the amount of the charge Electric Field (E) Fon q E = q Electric Field (E) Fon q = qE Calculate the electric field strength when a 25 N force is exerted on a charge of + 5.0 x -6 10 C Typical Field Strengths Field TV tube Spark r H orbital Value (N/C) 5 1 x 10 6 3 x 10 11 5 x 10 Electric Field Lines •Lines representing the force vectors in an electric field Electric Field Lines + Electric Field Lines - Electric Field Lines + - Electric Field Lines •Always point from positive to negative Electric Field Lines •Do not exist , but provide a model of a field The electric field between two parallel plates is uniform + - Electric Potential •The electric potential difference of charges measured in volts Electric Potential •As with heat, we can only measure potential difference (DV) Electric Potential Difference (DV) •The change in potential energy per unit charge Electric Potential Difference (DV) •The work done moving a charge thru a field charge Electric Potential Difference (DV) •Measured in J/C •J/C = volt (V) Electric Potential Difference (DV) W on q DV = q Electric Potential Difference (DV) DU = W Electric Potential Difference (DV) DUq DV = q Electric Potential Difference (DV) W on q DV = q Electric Potential Difference (DV) W = Fd Electric Potential Difference (DV) Fd on q DV = q Electric Potential Difference (DV) F DV = x d q Electric Potential Difference (DV) F E = q Electric Potential Difference (DV) DV = Ed Basic Equations •V = Ed •W = qV •F = qE Equipotential •When the electric potential difference is 0 Equipotential •Charge rearranges itself to reach equipotential Equipotential •When two spheres have the same charge, the larger one has lower electric potential Equipotential •When two spheres have the same electric potential, the larger one has the greater charge Equipotential •When a charged object comes in contact with a neutral one, the charge is equally distributed Equipotential •Because of the size of Earth, when objects touch Earth, their charge is passed to the Earth Grounding •When a charged object touches Earth, all its charge flows to Earth creating equipotential Electric Fields •All charges are on the outside of a conductor Electric Fields •In pointed object, the field strength is greatest at the point Capacitor •A device designed to store a charge Capacitance •The ratio of charge to electric potential difference Capacitance (C) q C = DV Farad (F) •Unit for capacitance measured in coulombs per volt: F = C/V Basic Equations •V = Ed •W = qV •F = qE •q = CV -6 10 A charge of 1.6 x C is stored to create a capacitance of -3 4.0 x 10 F acting over 2.0 mm. Calculate: V, E, F, & W -6 10 A charge of 1.5 x C is stored to create a capacitance of -3 4.0 x 10 F acting over 2.0 mm. Calculate: V, E, F, & W -4 10 A charge of 3.2 x C is stored to create a capacitance of 8.0 mF acting over 4.0 mm. Calculate: V, E, F, & W -6 10 Charge =1.6 x C -3 Force = 3.2 x 10 N Distance = 64 nm. Calculate: V, E, C, & W Calculate: -144 3.2 x 10 162 x 1.5 x 10 -256 8.0 x 10 175 7.5 x 10 122 x 4.0 x 10 = 144 10 Calculate: 3.2 x 162 x 1.5 x 10 -254 8.0 x 10 -175 7.5 x 10 125 x 2.0 x 10 =