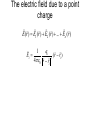* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 24 Electric Fields
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
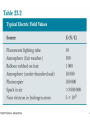
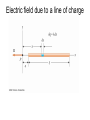
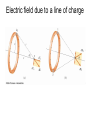
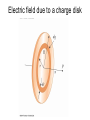
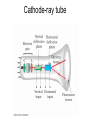
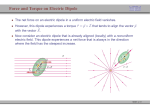
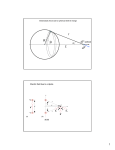
Chapter 24 Electric Fields 第二十四章 電場 Action at a distance kq1q2 F12 2 rˆ21 r21 k 9.0 10 Nm / C 9 r̂21 2 2 q1 q1 q2 q2 Another point of view -- Fields kq1q2 F12 2 rˆ21 r21 F12 q1 E2 (r21 ) kq2 1 q2 E2 (r ) 2 rˆ rˆ 2 r 40 r where E2 is the electric field generated by charge q2 and r is a position vector from the position of q2 to any point in space. 0 8.854 1012 C 2 / Nm2 Electric field lines Electric field lines The concept of electric field lines was originally due to Faraday who envisioned that the space around a charge is filled with “lines of force”. The field lines are originated from positive charges and terminated at negative charges, and they are unbroken in vacuum. The relationship between the electrical field and field lines Electric field lines with arrows indicate the local field directions, and their density in a plane perpendicular to the local field represents the magnitude of the local field. Suppose that there are N field lines originated from a positive charge q, then we have the density of field lines given by N / 4πr2 at a distance r from the charge. Note that if N = q / ε0 then we recover E = q / 4πε0 r2. Field lines repel each other Field lines are smooth The electric field due to a point charge E(r ) E1 (r ) E2 (r ) ... En (r ) Ei (r ri ) 3 40 r ri 1 qi Sample problem What is the electric field at point P? Sample problem What is the electric field at point P? The electric field due to an electric dipole y P E r -a r r q ( r r 4 0 r r r axˆ a x 3 r r r r 3 r axˆ Electric dipole moment: p q(r r ) 2qaxˆ p 2qa ) The electric field due to an electric dipole Along x-axis: For r xxˆ 2x p E 4 0 ( x 2 a 2 ) 2 1 2p x a : E 4 0 x3 x a: 1 1 ( a 2 x 2 ) p For x a : E 4 0 a(a 2 x 2 )2 The electric field due to an electric dipole r yyˆ zzˆ 1 p E 4 0 ( y 2 z 2 a 2 )3/ 2 In y-z plane: r a : Note that E 1 E 2 r 1 E 3 r 1 p 4 0 r 3 for net charge 0 for net charge 0 but net dipole moment 0 Electric field due to a line of charge Electric field due to a line of charge Electric field due to a line of charge Electric field due to a line of charge Electric field due to a charge disk A point charge in an electric field F qE Millikan oil-drop experiment (1910-1913) Cathode-ray tube Deflecting charge particles A dipole in an electric field pH2O 6.2 1030 Cm A dipole in an electric field There is no net force on a dipole. But there is a torque. qEa sin (qE )(a sin ) pE sin p E Potential energy of a dipole in a uniform electric field U pE cos U ˆ ( ) pE sin ˆ Home work Question (問題): 6, 8, 19 Exercise (練習題): 5, 10, 16 Problem (習題): 8, 18, 31, 32