* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Class 8 , Physics 260 Electric Charge, Electric Field (3) 1. For a
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
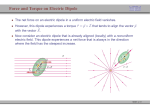
Class 8 , Physics 260 Electric Charge, Electric Field (3) 1. For a uniformly charged disk with charge/unit area σ, and radius R, with the x axis perpendicular to the disk and passing through the center of the circle, an integration finds the electric field to be 1 σ 1 − r Ex = 2 R 20 1+ 2 x When R −→ ∞, then Ex = σ 20 independent of x. 2. Electric Field Lines –a method for visualization of the electric field. Rules for drawing: (a) E-lines come out of + charge and go the − charge or to ∞. (b) The number of lines out of (+) Q is ∝ Q. (c) The tangent to and E-line is parallel to E at that point. (d) The number of lines/⊥ unit area is ∝ E (e) In electrostatics, no E-line may close on itself, with no charge. 3. An electric dipole which has equal positive and negative charges separated by a distance d has a diple moment p given by p = qd where d points from the negative to the positive charge. 4. In a uniform external electric field, a dipole experiences a torque given by τ =p×E 5. In a uniform external electric field, a dipole has potential energy U = −p · E 2