* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Voltage
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
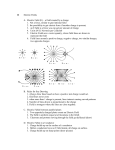
Voltage Volt The electric potential is related to the potential energy. U V q • Compare to test charge The unit of electric potential is the volt (V). • 1 V = 1 J/C q V d q E F Field Measure The electric field is most commonly measured in V/m. Show that this is consistent with a measurement in N/C. Use the definitions of N and J to link the two definitions of electric field. • 1 N/C = 1 (kg m / s2 ) / C • 1 N/C = 1 (kg m) / (s2 C) • 1 V/m = 1 (J/C) / m • 1 V/m = 1 (N m / C) / m=1 N/C • 1 V/m = 1 (kg m2 / s2) / (C m) • 1 V/m = 1 (kg m) / (s2 C) Electric Work A cathode ray tube accelerates electrons across a potential of 20 kV. Find the speed of the electrons at the screen. The potential can be converted to an energy. • qV = (1.6 x 10-19 C)(2 x 104 V) = 3.2 x 10-15 J. The potential energy becomes kinetic energy. • qV = ½ mv2 Solve for the speed v. • v = 8.4 x 107 m/s Uniform Field A uniform electrical field has U qEd the same magnitude and direction at all points. V Ed A charge moving parallel to the field lines changes potential by V = Ed. q U d q E F A charge moving perpendicular to the field lines has no change in potential. Conductor Potential There is no field within a conductor. • External field neutralized by polarization q A test charge at one end moved to the other end would not change potential. All points on a conductor are at the same potential. q Voltage Source A voltage source is called a battery. A battery attached to a conducting plate places the same potential across the plates. A uniform electric field exists between the plates. + - Internal Field A 12-V source is connected to parallel plates 2.0 mm apart. Find the magnitude of the field between the plates. The relationship between the field and voltage is V = Ed. • Solve for E = V/d The field is E = (12 V) / (0.002 m) = 6.0 kV/m. + - next