* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How Things Work
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electron mobility wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Density of states wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear physics wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
History of subatomic physics wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
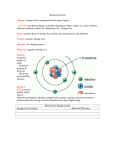
Xerographic Copiers Question: If you were to cover the original document with a red transparent filter, would the copier still be be able to produce reasonable copies? Observations About Copiers • • • • • • Copies consist of black stuff stuck on paper After jams, the stuff sometimes wipes off Copiers often run out of “toner” Copies are often warm after being made Copies are staticy, particular transparencies Some copies scan a light, some use a flash Electric Fields 1 • Two views of charge forces: • Charge/Charge: – Charge 1 pushes directly on Charge 2 • Charge/Field/Charge: – Charge 1 creates an “Electric Field” – Electric Field pushes on Charge 2 • Electric Fields are Real! Electric Fields 2 • An electric field is a structure in space that pushes on electric charge • The magnitude of the field is proportional to the magnitude of the force on a test charge • The direction of the field is the direction of the force on a positive test charge Quantum Physics 1 • All things travel as waves • All things interact as particles • Example 1: Light – Travels as waves – electromagnetic waves – Emitted and absorbed as particles – photons • Example 2: Electrons – Detected as particles – Travel as waves Quantum Physics 2 • Bosons: Photons – Many indistinguishable bosons can share a wave – Such sharing leads to lasers & superconductors • Fermions: Electrons, Protons, Neutrons – One indistinguishable fermion allowed per wave – “Pauli Exclusion Principle” Electrons in Solids • Only certain electron waves fit in a solid • Each allowed wave has an energy “level” • The electrons “occupy” levels two at a time – Electrons have two spin states: up and down – Spin-up is distinguishable from spin-down • Levels are filled from lowest to highest energy • Last (highest) filled level is the “Fermi level” Metals • The Fermi level has empty levels just above it • Like patrons in a partly fill theatre, electrons can move in response to electric fields Insulators • The Fermi level has no empty levels nearby • Like patrons in a full theatre, electrons can’t move in response to forces Semiconductors • Semiconductors are “poor insulators” • Valence & conduction bands have narrow gap • Like patrons in a theatre with a low balcony, electrons can hop into the balcony and move Photoconductors • In the dark, a semiconductor is insulating – When polarized, it has an electric field in it • In the light, a semiconductor may conduct – – – – Will conduct if photon energy can bridge gap Blue photons have more energy than red photons If conducting, electric field makes charges move In light, a “photoconductor” will depolarize Copier Structure Xerographic Process Question: If you were to cover the original document with a red transparent filter, would the copier still be be able to produce reasonable copies?