* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download INSIDE THE POWER PLANT - Illinois Institute of Technology
Magnetosphere of Saturn wikipedia , lookup
Edward Sabine wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
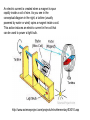
INSIDE THE POWER PLANT INSIDE THE POWER PLANT • Electricity is generated on a large scale at power stations and then transmitted through cables (called the National Grid) to factories and homes. • Power stations convert an energy resource into electrical energy. We will be exploring these types of resources in a few days • gcsescience.com INSIDE THE POWER PLANT • POWER PLANT • http://www.tampaelectric.com/Education/T EEDElecgen.html An electric current is created when a magnet is spun rapidly inside a coil of wire. As you see in the conceptual diagram in the right, a turbine (usually powered by water or wind) spins a magnet inside a coil. This action induces an electric current in the coil that can be used to power a light bulb. http://www.scienceproject.com/projects/intro/elementary/EX010.asp MAGNETS • All magnets have two ends, usually marked "north" and "south," • the fundamental law of all magnets: Opposites attract and likes repel • All magnets are surrounded by a magnetic field. http://science.howstuffworks.com MAGNETIC FIELD • A magnetic field is a region around the magnet where magnet materials experience a force. • The shape of the magnetic field around the magnet is shown by lines. Arrows on the lines point away from North and towards South to show the direction of the magnetic field. • The magnetic field is represented with the variable B and is measured in a unit called Tesla CURRENT INDUCES A MAGNETIC FIELD • Current running through a conductor will produce a magnetic field • This is why we saw a deflection on the compass needle in the Circuit lab. The magnetic field in the wires were interacting with the magnetic field of the compass Direction of Magnetic Field You can work out the direction of the field using your right clenched fist. Point your thumb upwards in the same direction as the current. The direction of the field is the same direction in which your fingers curl. gcsescience.com










![magnetism review - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002621376_1-b85f20a3b377b451b69ac14d495d952c-150x150.png)







