* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BUNDLE PROTOCOL
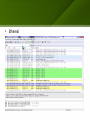
Access control wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Cross-site scripting wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Address space layout randomization wikipedia , lookup
Social engineering (security) wikipedia , lookup