* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Roman Expansion - raiderhistoryliese
Alpine regiments of the Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the mid-Republic wikipedia , lookup
Slovakia in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Berber kings of Roman-era Tunisia wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Hellenistic-era warships wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
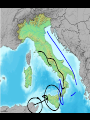
Cause and Effect: The growth of the Roman Republic and the changes that followed The Punic Wars -Carthage was an immensely powerful city in North Africa that controlled the Western Mediterranean. -Carthage boasted that the Mediterranean was a “Carthaginian lake,” in which people had to ask permission before washing their hands. The Punic Wars -After the Romans occupied Southern Italy, Carthage feared that they would try to capture Sicily, which contained several Carthaginian colonies and markets. -The Romans feared that the Carthaginian navy would close the Adriatic Sea and the Strait of Messina. What was the effect? The Punic Wars -The First Punic War-264 B.C. – 241 B.C.-The Romans created a naval fleet based on the wreckage of a Carthaginian ship. -They “board” the Carthaginian ships, fighting a land battle at sea. -Carthage pays an indemnity and gives up its claim to Sicily. The Punic Wars -The Second Punic War219 B.C. – 202 B.C. -Beginning in Spain, Hannibal marches through the Alps and into Italy, defeating the Roman army. -Hannibal had no siege equipment, so he could not attack the cities – Hannibal spent 15 years attacking the Italian countryside. The Punic Wars -The Second Punic War-Hannibal tried to win away some of the allies of the Roman Republic, but the policy of sharing citizenship with their allies kept them loyal to the republic – the Macedonian empire was one group that helped Carthage. -The Romans turned the tables by invading Africa and threatening Carthage. The Punic Wars -The Second Punic War-Rome defeats Carthage. -Carthage is forced to pay another large indemnity and cede control of their Spanish colonies to the Romans. What was the effect? Effects of the Second Punic War -Out of revenge for helping the Carthaginians, Rome starts a war with the Macedonians and defeats them in 197 B.C. – The Greek cities were now under Roman “protection.” -This leads to Rome’s conquest of the Seleucid empire. They have now gained supremacy in the east. -Carthage is no longer a threat. The Punic Wars Why the Third Punic War? -Some veterans of the Punic Wars and other important members of Roman society hated the Carthaginians, who they felt caused the previous Punic Wars. -Carthage was weaker, and Rome could crush them easily… The Punic Wars -The Third Punic War-149 B.C. – 146 B.C.-Using a flimsy excuse, the Romans attack the city of Carthage. -After their victory, the Romans destroyed what was left of the city, sold the population into slavery, and according to legends, covered the soil with salt. What was the effect of all of the Roman expansion? Government -Rome itself retained a republican form of government. -How did it change to accommodate the problems that come with governing a large territory? -The Senate controlled the army, finances, foreign affairs, and the new territories – the Senate was made up of Patricians… The aristocracy gains more power! Did this work well? Government -No-They did not grant citizenship to the people in these new territories (provinces) and they did not try to make them allies. -Instead, the Romans taxed the people of the provinces unmercifully. Government -Each province had a governor called a proconsul who was appointed by the senate and supported by the Roman army in the area. -The proconsul only served for one year and had no salary… What does this cause? Government -Corruption-The proconsuls collected bribes and ignored the needs of the people. -The censors would work with publicans, who would collect the taxes and give a fixed amount to the Roman empire… What would they do? Government -The publicans would tax higher rates than required and keep any money that they collected over the amount that they owed the Romans. Agriculture Rome has a lot of new territory… What does that mean for the small farmer back in Rome? -They play less of a role… why? Agriculture -The Roman government leased large estates made up of their new land (latifundia) to anyone that could afford their price. -Only wealthy people could afford the land. -Rome begins to depend on the provinces for grain. Agriculture -The hidden cost of the Punic Wars-Soldiers return home to their farms to discover their livestock is dead, their land is in ruins, and they don’t have enough money to bring it back to cultivation. What do they do? -They sell their land to the wealthy. Agriculture -The hidden cost of the Punic Wars-Where do the landless soldiers now go? -The city…the problem is there are not many jobs. They must now rely on the government for their food to stay alive. -Why not go back and serve in the army? Agriculture -The hidden cost of the Punic Wars-The republic only allowed landowners to fight. -The only thing that these veterans could do was sell their vote to the highest bidder. Social Change -The ideals of discipline and strength and loyalty to Rome have weakened among many of the now jobless masses. -Romans were now judged by wealth instead of by character. -Slave revolts became common – Spartacus led 70,000 slaves from 73 B.C.-71 B.C. in a brutal revolt that ended with his crucifixion. The Roman Empire is in need of reform…