* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Deflection with electric and magnetic fields
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup





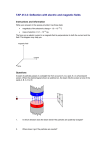
![NAME: Quiz #5: Phys142 1. [4pts] Find the resulting current through](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006404813_1-90fcf53f79a7b619eafe061618bfacc1-150x150.png)