* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The UNC-112 gene in Caenorhabditis elegans Encodes a Novel
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
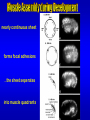
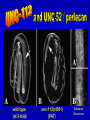
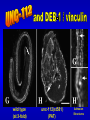
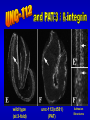
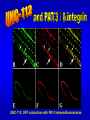
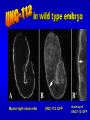
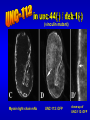
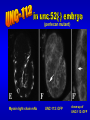
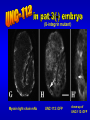
The UNC-112 gene in Caenorhabditis elegans Encodes a Novel Component of Cell-Matrix Adhesion Structures Required for Integrin Localization in the Muscle Cell Membrane Rogalski T.M., Mullen G.P., Gilbert M.M., Williams B.D., and D.G. Moerman Journal of Cell Biology, 150:253-264 Teresa Rogalski Research Scientist Department of Zoology QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Ph.D., Simon Fraser Gregory Mullen Department of Zoology UBC Mary Gilbert Department of Zoology UBC Benjamin D. Williams Associate Professor of Cell & Structural Biology University of Illinois Sc.B., Brown University (Biology) Ph.D., Yale University (Biology) Postdoc., Washington University School of Medicine Donald G. Moerman Professor B.Sc,, Ph.D., Simon Fraser Postdoc, Washington University School of Medicine Visiting Scientist, Max-Planck Institute for Biochemistry QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. This paper focuses on `s interactions with perlecan, vinculin, and ß-integrin Perlecan: located in the basement membrane Vinculin: binds actin & a-actinin ß-integrin: major structural TM component Muscle fibers need anchors …….. in order to contract! QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. nearly continuous sheet forms focal adhesions ..the sheet seperates into muscle quadrants Is a good neighbor? Perlecan ---> <--- ß-integrin <-- FA Vinculin ---> wild type (at 3-fold) unc-112(st581) (PAT) Adhesion Structures wild type (at 3-fold) unc-112(st581) (PAT) Adhesion Structures wild type (at 3-fold) unc-112(st581) (PAT) Adhesion Structures UNC-112::GFP colocalizes with PAT-3 immunofluorescence • Required for proper ß-integrin localization • Is needed to organize vinculin & perlecan* • However, vinculin does not need UNC-112 to localize itself with ß-integrin *but not required. Myosin light-chain mAb UNC-112::GFP close-up of UNC-112::GFP (vinculin mutant) Myosin light-chain mAb UNC-112::GFP close-up of UNC-112::GFP (perlecan mutant) Myosin light-chain mAb UNC-112::GFP close-up of UNC-112::GFP (ß-integrin mutant) Myosin light-chain mAb UNC-112::GFP close-up of UNC-112::GFP • Requires ß-integrin & perlecan for activation • Without them, cannot anchor FA complexes • Myosin is hopelessly lost without UNC-112 Human Ortholog of (kindlin-1) …also plays a role in proper attachment of actin to QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. vinculin Human Ortholog of (kindlin-1) Otherwise…… QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (LZW) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Not required for: -- Polarization of muscle cell membrane -- Focal Adhesion (FA) complex formation Required for: -- Neat and orderly arrays of FA complexes -- Proper attachment of actin to FAs -- Any Attachment of Myosin to FAs