* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells to Body Systems
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
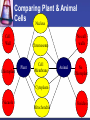
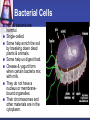
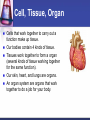
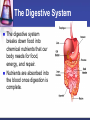
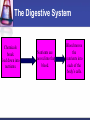
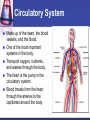
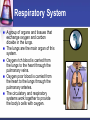
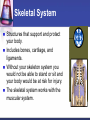
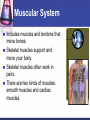
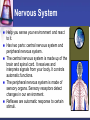
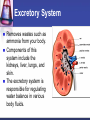
Cells to Body Systems Cells The basic unit of function in living things. Most cells can only be seen under a microscope; they are microscopic. All organisms (any living thing that maintain life) are made up of cells. Some organisms have only one cell. Most plants and animals are made of many cells. Different types of cells have different jobs. Cells work together to carry out life processes. Plant & Animal Cells All cells have similar structures. Every cell is surrounded by a cell membrane. Most cells have a nucleus that directs all of the cell’s activities. The cytoplasm is a jellylike material that separates the cell membrane and the nucleus. Comparing Plant & Animal Cells Nucleus Cell Wall Chloroplast No cell walls Chromosome Plant Cell Membrane Animal No Chloroplast Cytoplasm Vacuole Mitochondria Vesicles Bacterial Cells Not all bacteria are harmful. Single-celled. Some help enrich the soil by breaking down dead plants & animals. Some help us digest food. Cheese & yogurt form when certain bacteria mix with milk. They do not have a nucleus or membranebound organelles. Their chromosomes and other materials are in the cytoplasm. Protist Some are single-celled organism. A simple organism with a nucleus and organelles. Plant-like protists have cell walls and chloroplasts. Animal-like protists have no cell walls or chloroplasts. Diatomas, algae, and amoeba are protists. Cell, Tissue, Organ Cells that work together to carry out a function make up tissue. Our bodies contain 4 kinds of tissue. Tissues work together to form a organ (several kinds of tissue working together for the same function). Our skin, heart, and lungs are organs. An organ system are organs that work together to do a job for your body. The Digestive System The digestive system breaks down food into chemical nutrients that our body needs for food, energy, and repair. Nutrients are absorbed into the blood once digestion is complete. The Digestive System Chemicals break food down into nutrients. Nutrients are moved into the blood. Blood moves the nutrients into each of the body’s cells. Body Organization Our body is organized to keep us alive and healthy. Each cell works to keep itself healthy. Cells work with other cells to form tissue. Tissues work together in organs. Organs work together in systems. Systems work together to keep our body functional. Circulatory System Made up of the heart, the blood vessels, and the blood. One of the most important systems in the body. Transport oxygen, nutrients, and wastes through the body. The heart is the pump in the circulatory system. Blood travels from the heart through the arteries to the capillaries around the body. Circulatory System: Blood Flow Blood flows from the lungs to the heart through veins. From the heart, blood flows through arteries. From the arteries, it flows through capillaries. From capillaries, it flows back to the heart through veins. Respiratory System A group of organs and tissues that exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs. The lungs are the main organ of this system. Oxygen rich blood is carried from the lungs to the heart through the pulmonary veins. Oxygen poor blood is carried from the heart to the lungs through the pulmonary arteries. The circulatory and respiratory systems work together to provide the body’s cells with oxygen. Respiratory System: Oxygen from the air to our blood Oxygen is inhaled when we breathe air. Oxygen travels town the trachea to the bronchi and then to alveoli. Next, it passes into the capillaries. Then, it is carried by red blood cells. Skeletal System Structures that support and protect your body. Includes bones, cartilage, and ligaments. Without your skeleton system you would not be able to stand or sit and your body would be at risk for injury. The skeletal system works with the muscular system. Muscular System Includes muscles and tendons that move bones. Skeletal muscles support and move your body. Skeletal muscles often work in pairs. There are two kinds of muscles: smooth muscles and cardiac muscles. Nervous System Help you sense your environment and react to it. Has two parts: central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. It receives and interprets signals from your body. It controls automatic functions. The peripheral nervous system is made of sensory organs. Sensory receptors detect changes in our environment. Reflexes are automatic response to certain stimuli. Excretory System Removes wastes such as ammonia from your body. Components of this system include the kidneys, liver, lungs, and skin. The excretory system is responsible for regulating water balance in various body fluids. Video Questions What are the parts of plant and animal cells? What are the different systems and roles of multi-cellular organisms? How do cells work together as tissues? What are the processes of formation from tissues to organ systems? What types of systems and roles are in the human body? How do those body system interact?