* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slajd 1 - Naslovnica - Web Stomatološkog fakulteta
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Body snatching wikipedia , lookup
Circulating tumor cell wikipedia , lookup
Human digestive system wikipedia , lookup
History of anatomy wikipedia , lookup
Lymphatic system wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terminology wikipedia , lookup
SCHOOL OF DENTAL MEDICINE
UNIVERSITY OF ZAGREB
Lidija Štefić
ENGLISH IN DENTAL MEDICINE I
WORD FORMATION IN ENGLISH
DERIVATION
CONVERSION
COMPOUNDING
BORROWING
DERIVATION
AFFIXATION
AFFIXES
SUFFIXES
PREFIXES
ROOT (STEM)
COMBINING
WORD
BASIC WORD STRUCTURE
Word root:
gingiv/al
root (gums)
Suffix:
gingiv/itis
Prefix::
suffix (inflammation)
sub/gingiv/al
prefix (below)
Combining word::
prefix
electr/o/cardi/o/gram
root
combining vowel
suffix
SUFFIXES IN DENTAL MEDICINE
a word added at the end of a word or word base (root)
to change its meaning.
DERIVE FROM
Greek
Latin
WR
SUFFIX
gingiv +
arthr +
-itis
-algia
WR
+O
SUFFIX
pulp
+O
+ -tomy
NEW TERM USED IN
DENTISTRY OR MEDICINE
gingivitis
arthralgia
NEW TERM USED IN
DENTISTRY OR MEDICINE
pulpotomy
SURGICAL PROCEDURE SUFFIXES
Incision
-ectomy (surgical removal, excision)
apiectomy -
the ablation of the root end of a tooth
-o/centesis (surgical puncture)
amniocentesis surgical perforation of the uterus to
obtain amniotic fluid
-o/stomy (forming an opening)
esophagostom the surgical creation of an opening
yinto the esophagus
-o/tome (instrument to cut)
osteotome -
a chisel like knife for cutting bone
-o/tomy (to cut into)
tracheotomy -
incision of windpipe
Plastic operations (repair, rebulid, reconstruct, bind)
-desis
arthrodesis - surgical fixation of a joint
-o/rrhaphy (suture)
splenorrhaphy - surgical repair of the
spleen
-o/pexy (fixation,
suspension)
splenopexy - surgical fixation of a
mobile spleen
-o/plasty (formation,
plastic
repair)
osteoplasty - plastic surgery involving a
bone
Refracturing, loosening, crushing
-o/clasis (to break down,
refracture)
osetoclasis - the surgical
fracture or refracture of
bones
-o/lysis (loosen, free form
adhesions,
destruction)
enterolysis - the
operative division of
adhesions between loops
of intenstine of or
between the intestine
and
abdominal wall
-o/tripsy (to crush)
neurotripsy - surgical
crushing of a nerve
DIAGNOSTIC AND SYMPTOMATIC SUFFIXES
-algia (pain)
odontalgia -
toothache
-o/cele (hernia, swelling)
nephrocele -
hernial protrusion of a kidney
-o/dynia (pain)
odontodynia -
toothache
-ectasis (dilatation, expansion)
bronchiectasis
-
chronic dilatation of the bronchi
-emia (blood condition)
hyperemia -
an excess of blood in a body part
-o/gen (beginning, origin) pathogen -any disease - producing
microorganism
-o/gram (a writing, record)
roentgenogram - a photograph taken with the x-rays
-o/graph (to write, record)
cardiograph -
a technique by means of which
roentgenograms of the heart can be made
at any chosen phase of its cycle.
-iasis (condition, formation of, presence of)
psoriasis -
a chronic skin disease characterized by
scaly red dish patches
-sis (state of, condition)
dysgenesis -
state of deterioration of hereditary
qualites of the stock
-itis (inflammation)
stomatitis -
a general inflammation of the mouth
-o/logy (study of)
odontology -
the study of the teeth
-o/malacia (softening)
osteomalacia -
a condition marked by softening of the
bones
-o/megaly (enlargement)
acromegaly -
enlargement of the extremities of the
skeleton, the nose, jaws fingers and toes
-o/meter (measure)
dynamometer -
an instrument for measuring forces or
power
-oma (tumor, mass)
odontoma -
tumor of a tooth, although it doesn’t show
all the features of a tumor. It consists of the
calicified dental tissues
-opsy (process of viewing)
autopsy -
an examination and dissection of a dead
body to discover the cause of death,
damage done by disease.
-o/pathy (disease)
trombocytopathy - a very rare disease of unknown etiology
where there is a tendency to bleeding.
-o/penia (decrease, deficiency)
leukocytopenia
-
deficiency in the number of leukocytes
-osis (abnormal condition, increase-used only with blood cells) e.g.
leukocytosis
sialosis -
chronic swelling of the salivary glands
-phagia (eating)
dysphagia -
difficulty in swallowing
-phasia (speech)
dysphasia -
impairment of the ability to speak
-plegia (paralysis, stroke)
paraplegia -
paralysis of the legs and lower part of the
body
-phobia (morbid fear)
aerophobia -
an abnormal fear of air, especially drafts
metroptosis -
downward displacement or prolapse of the
uterus
-o/ptosis
-o/rrhage (burst forth)
hemorrhage -
excessive blood flow
-o/rrhea (discharge, flow)
dysmenorrhea -
painful or difficult menstruation
-o/clerosis (hardening)
arteriosclerosis -
thickening and loss of elasticity of arterial
walls
-scope (instrument to visually examine)
endoscope -
an instrument for examining visually the
inside of a hollow organ of the body, as the
bladder or rectum
SUFFIXES: ADJECTIVE ENDINGS
The adjective endings that mean “pertaining to” are:
-ac
cardiac (heart)
-al
gingival (gums)
-ar, -ary
salivary (saliva)
-ic
dermic (skin)
-ical
apical (apex)
-ous
mucous (mucosa)
-(t)ic
lymphatic (lymph)
SUFFIXES: NOUN ENDINGS
-coccus
bacteria
streptococcus (berry shaped bacteria)
-cyte
cell
thrombocyte
-ole
little, small
arteriole - little artery
hypertrophy (cells increase in size, not
number)
-trophy
-ule
little, small
nodule - little node
-ist
specialist
dentist - a specialist in dentistry
-iac
an individual
affected by a
certain disase
hypohondriac - an invidual who thinks
he is ill
-ia
abnormal condition amnesia - forgetfulness
-is
forms the noun
from the root
cutis - skin
-ism
abnormal
condition, state of
being
alcoholism
PREFIXES IN DENTAL MEDICINE
at the beginning of a word
DERIVE FROM
Greek
Latin
PREFIXES OF DIRECTION
Prefix
Meaning
ab-
from,away from
ad-
to, toward, near
circum –
peri-
around
Example
ab/normal
usual, regular
ad/sternal
breast plate
circum/renal
kidney
peri/odontal
tooth
Prefix
ecex-
ectoexoextra-
Meaning
through, across
outside
Example
ec/tropia
place
ex/cision
to cut
ecto/derm
skin
ex/odontics
tooth
extra/cellular
cell
Prefix
Meaning
endoIntra-
in, within
parpara-
near,
beside,beyond
supersupra-
above
excessive
Example
endo/cranial
skull
intra/dental
tooth
para/nasal
nose
super/acidity
acidity
supra/molecular
molecule
Prefix
Meaning
ultra-
beyond,excesive
diapertrans-
trough, across
Example
ultra/sonic
sound
dia/rea
flow
per/cutaneos
skin
trans/urethral
urethra
PREFIXES OF POSITION
Prefix
ambiamphi-
anteanter/oprepro-
Meaning
both,both sides
on both sides
before, in front of
Example
ambi/lateral
side
amphi/cranial
skull
ante/febrile
antero/septal
Septum
pre/operative
Operation
pro/nephros
kidney
Prefix
dextr/o-
Meaning
right, to the right
dors/o-
back
epi-
upon
hypo-
infrasub-
under below
beneath, under
Example
dextr/o/rotatory
rotation
dors/o/ventral
belly
epi/cranial
skull
hypo/dermic
skin
infra/sonic
sound
sub/lingual
tongue
Prefix
inter-
Meaning
between
later/o-
to the side of
mes/omedi-
in the middle of
retropost-
after,backward
postero-
located, behind
sinistr/o-
left,to the left of
Example
inter/dental
tooth
latero/abdominal
stomach
mes/o/dermic
skin
retro/cervical
cervix(neck)
postero/lateral
To the side of
sinistr/o/dextral
to the right
PREFIXES OF NUMBER AND MEASUREMENT
Prefix
Meaning
Example
micro-
small
micro/stomatous
mouth
macro-
large
macro/cyst
hyper-
over,above,excessive
hyper/sensitivity
hypo-
under,below,deficient
primi-
first
hypo/glossal
tongue
primi/para
to bear off spring
Prefix
Meaning
unimono-
one
bidi-
two
hemi-
half
semi-
partial
Example
uni/lateral
side
mono/nucleus
kernel
bi/lateral
side
di/phy/odont
leaf, tooth
hemi/plegia
paralysis
semi/lunar
moon
Prefix
Meaning
multipoly-
many
tri-
three
quadri-
four
Example
multi/lateral
side
poly/phobia
fear
tri/cephalus
head
quadry/plegia
paralysis
PREFIXES OF COLOUR
Prefix
Meaning
Example
albalbuminoleuc/oleuk/o-
white
albin/ous
contain
leuc/emia
blood condition
chlor/o-
green
chlor/emija
grey
glauc/oma
swelling
polio/myel/itis
glauc/opoli/o-
Prefix
Meaning
Example
yellow
cirrh/osis
abnormal condition
xanth/emia
cyan/o-
blue
cyan/o/dermia
skin
melan/o-
black
cirrh/oxanth/o-
erythr/orube/o-
purpur/o-
red
purple
melan/oma
tumor, mass
erythr/o/cyte
cell
rube/osis
abnormal condition
purpur/ic
pertaining to
PREFIXES OF NEGATION
Prefix
a–
(used before a
consonant)
an(used before a
vowel)
arimindis-
Meaning
Example
a/pnea
without, not, a lack of
breath
not
ar/rhythmia
rhythm
im/mature
in/somni/ac
sleep
dis/functional
MISCELLANEOUS PREFIXES
Prefix
anticontra-
bradytachydys-
Meaning
Example
against
anti/bacterial
Bacteria
contra/ception
fertilization
slow
brady/cardia
heart
rapid
tachy/cardia
heart
Bad,paniful,difficult
Dys/phagia
swallowing
Prefix
euheter/o-
homohydro-
mal-
meta-
Meaning
Example
good, easy
eu/pnea
breathing
different
heter/o/cellular
cell
same
homo/sexual
sex
water
hydr/o/cephalus
head
ill, bad, poor
after,over,change
mal/nutrition
food substances
meta/plasia
abnormal (change)
Prefix
panpseudo-
scler/o-
symsyn-
Meaning
Example
all
pan/hyster/ectomy
uterus/removal
false
pseudo/mening/itis
meninges inflammation
hard
scler/osis
condition of
union, together
sym/podia
foot
syn/chilia
lips
COMBINING FORMS
Combining
form
Meaning
Terminology
cyt/o
all
cytology
cephal/o
head
cephalic
-ic means pertaining to
physi/o
nature
physiology
study of functions of the
living organism
hem/o
blood
hematoma
-oma means tumor or mass
Meaning
crin/o
to secrete
endocrine glands
endo-means within
derm/o
skin
hypodermic
hypo-means below, under
gingiv/o
gums
gingivitis
-itis means inflammation
cerebr/o
brain
cerebrum
cerebral
-al means pertaining to
gen/o
producing
pathogenic
produced by patho-means disease
gnos/o
knowledge
diagnosis
-dia-means complete;
-sis means state of. A diagnosis
is
made
after
sufficient
information has been obtained
about the patient’s condition
cardi/o
heart
cardiology
sarco/o
flesh
sarcoma
path/o
disease
pathological
orth/o
straight,
regular,
correct
orthodontist
odont means tooth
-ist means a specialist
bi/o
life
biopsy
-opsy means process of viewing
oste/o
bone
osteodynia
-dynia means pain
ANATOMY
Anatomy (from the Greek ἀνατομία anatomia, from ἀνατέμνειν ana:
separate, apart from, and temnein, to cut up, cut open)
is a branch of biology
It is the study of exernal and internal structures
and the physical realationships
between body parts
Macroscopic (gross)
-surface
-regional
systemic
Microscopic
-cytology
-histology
HYSTORY OF ANATOMY
Hippocrates of Kos
(Greek: Ἱπποκράτης)
Claudius Aelius Galenus
(AD 129 – 200)
ca. 460 BC - ca. 370 BC
Canon of Medicine
Ibn al-Nafis
1213-1288
1484
Leonardo da Vinci
Anatomy Lesson of dr.Nicolaes Tulp
1632
Rembrandt
1606 - 1669
1452 - 1519
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek
1632 - 1723
Robert Hooke’s microscope
The scanning electron microscope (SEM)
Anatomy employs two chief methods of study - the systemic and
topographic.In the former the body is regarded as consisting of systems
and organs.
The divisions of systemic anatomy are:
a. Osteology, the description of the skeleton
b. Arthrology, the description of the joints
c. Myology, the description of muscles and accessory
structures
d. Splancnology, the description of viscera
e. Angiology, the description of organs of circulation
f.
Neurology, the description of the nervous system
g. Esthesiology, the description of the sense organs
Dental medicine takes into consideration other branches of systemic
anatomy such as : embriology, genetics, endocrinology and dermatology.
Pathological anatomy is the study of diseased organs.
sections of normal anatomy applied to various purposes receive
special names such as
medical, surgical, ginaecological, artistic and superficial anatomy
Structural Organisation of the Body
Organs, Systems
Body Cavities
Organs and Systems
Tissues Patterns Various Organs
Organs = several kinds of tissue
viscera (lat.) = internal organs (sing. viscus)
Systems = groups of organs working
together and performing complex functions
Gastrointestinal System
•Mouth, pharynx,
• oesophagus, stomach,
• intestines
(small and large),
•liver, gallbladder, pancreas
Excretory System
Kidneys, ureters,
urinary bladder,
urethra
Respiratory System
Nose, pharynx, larynx,
trachea, bronchial
tubes, lungs
Reproductive System
Female: Ovaries,
fallopian tubes,
uterus, vagina,
mammary glands
Reproductive System
Male: testes
and associated tubes,
urethra, penis,
prostate gland
Endocrine System
Thyroid gland,
pituitary gland, sex glands,
adrenal glands,
pancreas,
parathyroid glands,
pineal gland, thymus gland
Nervous System
Brain, spinal cord,
nerves, and collection
of nerves
Cardiovascular System
Heart, blood vessels
(arteries, veins and
capillaries),
lymphatic vessels
and nodes,
spleen, thymus gland
Muscular System
Muscles
Skeletal System
Bones and joints
(articulations)
Integumentary System
Skin, hair, nails and
associated glands
(sweat or sudoriferous
and sebaceous
or oil glands)
Body Cavities
Body cavity = space
within the body
containing the
internal organs (viscera).
Cranial Cavity
Brain
Thoracic Cavity
Subdivided into:
-Pleural Cavities:
area surrounding the
lungs
-The Mediastinum:
area between the
lungs; contains heart,
aorta, trachea,
oesophagus, and
thymus gland
Abdominal Cavity
Stomach, small and large
intestines, spleen, liver,
gallbladder, pancreas,
kidneys
Surrounded by
peritoneum
Pelvic Cavity
Urinary bladder,
urethra, ureters;
uterus and vagina
in the female
Spinal Cavity
Spinal cord and
nerves of the spinal
cord
Glossary
tissue = tkivo
cavity = šupljina
gallbladder = žučni mjehur
pancreas = gušterača
spleen = slezena
thymus gland = prsna žlijezda
thyroid gland = štitnjača
MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
•BONES
•JOINTS
•MUSCLES
BONES
Bones are complete organs, composed
of connective tissue called osseous tissue
Dense connective tissue includes the
cartilage and bone
It consists of osteocytes surrounded by
intercellular substance filled with
calcium salts
It is composed of an outer hard layer
and an inner,spongy core.
Compact tissue- forms the outer layer of
bones, it is arranged in concentric
layers with a hollow centre which carries
blood vessels and nerves.
The inner spongy core- forms the inside of
bones, it has the yellow and red bone marrow.
- the yellow bone marrow stores fat cells
(leucocytes).
- the red bone marrow contains red cells
(erythrocytes).
External surface of bone is covered by
periosteum- it has the function
of feeding the bone
Several hormones regulate the activity of the bone
cell
1) Osteoblasts- they are immature
osteocytes which produce the bony tissue
that replaces cartilage during ossification
2) Osteoclasts- they reabsorb bony
tissue thus enlarging the inner bone
cavity so that the bone does not
become overly thick and heavy
- parathyroid gland stimulates
osteoclasts to remove bone and to
stimulate osteoblasts to build up the
bone
It secretes a hormone to release
calcium from bone, bones become weakened
due to loss of calcium.
CRANIAL BONES
•Frontal
•Parietal
•Temporal
•Occipital
•Sphenoid
•Ethmoid
FACIAL BONES
•Nasal
•Lacrimal
•Maxillary
•Mandibular
•Zygomatic
•Vomer
The Mandible
The Maxilla
The Palate
JOINTS
junctions (meeting places called articulations)
between two or more bones.
SYNARTHROSES
DIARTHROSES
TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT (TMJ)
FOUR MOVEMENTS OF TMJ:
Elevation
Depression
Protraction
Retraction
MUSCLES
from Latin musculus, diminutive of mus "mouse"
Myology is the branch of anatomy dealing with the muscles,
muscular tissue components, structure and functions.
Striated - Voluntary
Smooth - Involuntary
Cardiac
MASTICATORY MUSCLES
Temporal Muscle
Masseter Muscle
Lateral (External)
Pterygoid Muscle
Digastric Muscle
(Anterior Portion)
Temporal Muscle
Masseter Muscle
Lateral (External) Pterygoid Muscle
Digastric Muscle (Anterior Portion)
FACIAL MUSCLES
Orbicularis oris
– the sphincter of the mouth
The buccinator
- a deep muscle of the cheek
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
NERVE TISSUE
Neuroglia
Neurons
Neuron
Dendrite
Axon Terminal
Node of
Ranvier
Soma
Schwann cell
Nucleus
Axon
Myelin sheath
SYNAPSE
Greek "syn-" ("together") and "haptein" ("to clasp").
synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons
signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or
glands.
THE BRAIN
CRANIAL NERVES
There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves.
Olfactory I
Optic II
Oculomotor III
Trochlear IV
Trigeminal V
Abducens VI
Facial VII
Auditory (vestibulocochlear) VIII
Glossopharyngeal IX
Vagus X
Spinal Accessory XI
Hypoglossal XII
THE CIRCULATORY AND
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
BLOOD AND OTHER BODY FLUIDS
Fluids constitute over
half of an adult’s weight
under normal conditions
These fluids are vital
in the transport of
nutrients to all cells
Blood is composed of:
liquid (plasma) – 55%
formed elements ( erythrocytes,
leukocytes and platelets) – 45 %
Plasma consists of
about:
- 90% of water
7% proteins
less than 1%
inorganic salts,
organic substances,
dissolved gases,
hormones, antibodies
and enzymes
Many important proteins
such as serum, albumin,
gamma globulin and
fibrinogen are dissolved
in the plasma
Fibrinogen is essential in the clotting process
All blood cells originate from hemocytoblasts
They change from undifferentiated form into
specialized or differentiated
Hematopoiesis: :
Blood transports oxygen from the lungs to
the body tissues, and carbon dioxide
from the tissues to the lungs:
Erythrocytes
The great majority of
all blood cells
35 trillion in the
average adult
Total surface area almost
the size of a football field
Hemoglobin enables carrying oxygen from the
lungs to the tissues
Red blood cells are
stored in the spleen
They live for about
110 to 120 days
About 180 million
erythrocytes are
destroyed every
minute
Leukocytes
Body’s primary
defense against
Infections
These cells are larger
than erythrocytes and
fewer in number
Blood has about 8000
leukocytes per cubic
millimeter
Classification of leukocytes
1. Granulocytes ( neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils)
2. Agranulocytes (monocytes, lynphocytes)
Neutrophils form
about 70%, and
limphocytes about
20% of the total
number
Platelets (thrombocytes)
Small clear disk-shaped bodies
About 1/3 the size of erythrocytes
25000 platelets per one cubic millimeter of blood
They initiate blood clotting
Platelets disintegrate
and adhere to the
edges of the injured
tissue
Blood coagulation (clotting)
The process by which the body
prevents blood loss
Bleeding generally stops within
5 minutes
A thrombus can form
within a vessel
Defects in blood vessels
(owing to injury or disease)
•Anemia
•Neutropenia
•Human immunodeficiency
virus (HIV)
•Leukimia
•Thrombocytopenia
•Hemophilia
BLOOD TRANSFUSION
BLOOD GROUPS
Four main blood groups
Type O = universal donors
Type AB = universal recipients
Rhesus factor - Rh
Another important factor, called Rh factor must
also be considered in blood typing. This is a
very complex system : 8 principal variants of
the Rh factor are known, and there are others
not yet identified and grouped. For practical
reasons there are 2 main groups of Rh types:
Rh positive
Rh negative
Blood diseases
Blood parasites
Christmas disease
Hemophilia
Malaria
Septicemia
Vitamin K deficiency
Hemoglobin C,S,E disease
Vitamin K deficiency
Anemia
Malaria
Hemophilia
THE CIRCULATORY AND
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
The cardiovascular system is composed of the
heart, blood vessels and blood. The circulatory
system consists of the heart, blood vessels and
lymphatics. This system transports food,
oxygen, and other vital substances to all body
cells and picks up waste products for disposal.
THE HEART
The heart is a hollow, muscular organ that
pumps blood through the blood vessels. It is
enclosed in a fibrouserous sac called
pericardium. The heart beats over 100.000
times per day. It weights about one half pound
and is the size of clenched fist
The heart has three distinctive layers of
tissue:
The endocardium
The myocardium
The epicardium
The heart is divided into four
chambers:
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Left atrium
Left ventricle
BLOOD VESSELS
ARTERIES
carry blood from the heart to the body tissues and organs
VEINS
carry blood back to the heart from body organs and tissues
CAPILLARIES
connect arterioles to venules.
LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
Lymph fluid
Capillaries
Lymphatic vessels
Lymphatic ducts
Lymph nodes
FUNCTION
Transporting fluids from tissues back to the bloodstream
Aiding in the control of infection caused by microorganisms
Conveyance of lipids or fats away from the digestive organs
Lymph nodes of the human head and neck
Regional lymph tissue
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
The digestive system is
basically a long, muscular
tube that begins at the
mouth and ends at the anus
The functions of the
digestive system are
threefold
Digestive enzymes are substances that speed up
chemical reactions and help in the breakdown of
complex nutrients
Digestion can be defined as a complete process of
changing the chemical and physical composition of food
in order to facilitate assimilations of the nourishing
ingredients of flood by the cells of the body
The gastrointestinial (GI) tract begins at the oral cavity or
mouth
THE MOUTH
The mouth is the first division of the digestive tube
and is separable into two parts, smaller external
part, the vestibule formed by the lips cheek, gums
and teeth and a larger part, the mouth proper (oral)
cavity behind the gums and teeth
Lips and cheeks
Lips are a visible body part at the mouth of humans
and many animals.
Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food
intake , and in the articulation of speech,
as a tactile sensory organ as an erogenous organ used
in kissing and other acts of intimacy.
Cheeks (Latin: buccae) constitute the area of the
face below the eyes and between the nose
and the left or right ear.
Gums and teeth
Gingiva are part of the soft tissue lining of the mouth.
They surround the teeth and provide a seal around them.
Compared with the soft tissue linings of the lips and cheeks,
most of the gingiva are tightly bound to the underlying bone
and are designed to resist the friction of food passing
over them. Healthy gingiva is usually coral pink,
but may contain physiologic pigmentation.
Changes in color, particularly increased redness,
together with edema and an increased tendency to bleed,
suggest an inflammation (gingivitis)
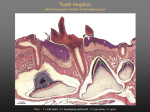
Teeth (singular, Tooth) are small whitish structures
found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates
that are used to tear, scrape, milk and chew food
Humans usually have 20 primary teeth
(also called deciduous, baby, or milk teeth)
and 32 permanent teeth. Among primary teeth,
10 are found in the (upper) maxilla and the other
10 in the (lower) mandible.
Teeth are classified as incisors, canines,premolars
and molars .
The main functions of the teeth:
Incisors = cutting
Canines = tearing
Premolars = crushing
Molars = grinding
The tongue
The tongue is skeletal muscle on the floor of the
mouth that manipulates food for
chewing and swallowing (deglutition).
The main functions of the tongue:
•It moves food around in the mouth
•It begins swallowing action (deglutition)
•It aids in speech production
•It provides the equipment for taste sensation