* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CV SYSTEM for GCSE PE lesson Year 11 tomorrow
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
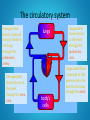
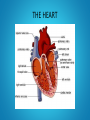
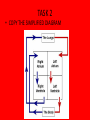
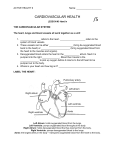
Year 11 GCSE PE THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM OBJECTIVES • TO KNOW THE JOURNEY OF BLOOD THROUGH THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM • TO UNDERSTAND HOW THE HEART WORKS • TO BE ABLE TO LABEL A DIAGRAM OF THE HEART QUICK QUIZ 1. NAME THE AGONIST AT THE ELBOW WHEN THROWING A JAVELIN 2. WHAT IS A SYNERGIST? 3. WHAT TYPE OF MUSCLE ACTION IS THE DOWN PHASE OF A PRESS UP? 4. NAME THE AGONIST AT THE SHOULDER FOR THIS MOVEMENT ANSWERS 1. TRICEPS 2. A MUSCLE THAT ASSISTS THE AGONIST BY SUPPORTING THE BODY OR JOINT DURING MOVEMENT 3. ISOTONIC ECCENTRIC 4. PECTORALS What is made up of the Cardiovascular system What is the CARDIOVASCULAR system? The HEART, LUNGS , BLOOD and BLOOD VESSELS + + BLOOD is pumped around the body by the HEART through the BLOOD VESSELS BLOOD performs two main functions as it travels around the body: – 1. supply the body with oxygen and nutrients – 2. to remove waste products such as carbon dioxide Why is the CV system important Why is the CV system important? The HEART is the most important muscle in the body A strong CV system often means that you have good cardiovascular fitness This means that you have the ability to exercise the whole body for long periods of time CV fitness is important for everyone, not just sports people! Sport and the CV system • IN SPORT, THE CV SYSTEM DELIVERS OXYGEN TO OUR WORKING MUSCLES and organs Blood vessels that run throughout the body allow the blood to travel everywhere Let’s look closer at the path of the blood... The circulatory system Deoxygenated blood is pumped from the heart to the lungs through the pulmonary artery. Deoxygenated blood returns to the heart through the vena cava. lungs Oxygenated blood returns to the heart through the pulmonary vein. Oxygenated blood is pumped at high pressure from the heart to the body through the aorta. body’s cells The double circulatory system The pulmonary circulation carries: lungs deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs oxygenated blood back from the lungs to the heart, ready to be pumped out to the body. The systemic circulation carries: oxygenated blood to the rest of the body through the arteries deoxygenated blood back to the heart through the veins. body’s cells THE HEART TASK 1 • YOU HAVE 5 MINUTES TO LABEL YOUR HEART DIAGRAM BILLY THE BLOOD CELL • BILLY HAS NO OXYGEN TO GIVE • HE IS IN THE VENA CAVA • HE NEEDS TO COLLECT OXYGEN TO GIVE IT AWAY TO MARTY THE MUSCLE, SO HE MAKES HIS WAY INTO THE RIGHT ATRIUM • HE THEN PASSES DOWN INTO THE RIGHT VENTRICLE • HE NOW GETS PUMPED THROUGH THE PULMONARY ARTERY TO THE LUNGS TO PICK UP OXYGEN • NOW HE HAS OXYGEN HE GOES BACK TO THE HEART VIA THE PULMONARY VEIN • BILLY NOW RETURNS TO THE HEART INTO THE LEFT ATRIUM • HE PASSES DOWN INTO THE BIGGEST CHAMBER, THE LEFT VENTRICLE • FROM HERE BILLY CAN NOW BE SENT ON HIS WAY TO MARTY • HE IS PUMPED THROUGH THE AORTA TO THE WORKING MUSCLES TASK 2 • COPY THE SIMPLIFIED DIAGRAM DEFINITIONS • HEART RATE (HR): THE NUMBER OF TIMES THE HEART CONTRACTS IN 1 MINUTE • STROKE VOLUME (SV): THE AMOUNT OF BLOOD EJECTED FROM THE HEART IN ONE BEAT • CARDIAC OUTPUT (Q): THE AMOUNT OF BLOOD EJECTED FROM THE HEART IN 1 MINUTE • Q = HR X SV • EG. HR = 72BPM, SV = 70ML • Q = 72 X 70 = 5040ML • = 5 LITRES TASK 3 • WORK THROUGH THE FOLLOWING EXAMPLES: • HR = 110, SV = 80ML, WHAT IS Q? • HR = 85, Q = 5250ML, WHAT IS SV? • SV = 75, Q = 6000ML, WHAT IS HR? ANSWERS • 110 X 80 = 8800ML = 8.8L • 5250 / 85 = 62ML • 6000 / 75 = 80BPM HOMEWORK On wikispaces please complete by next Monday without fail Diagram: HANDOUT Colour in and label the diagram of the cardiovascular system Label the following; The heart The lungs The body Colour the corrects sides; De-oxygenated blood = blue Oxygenated blood = Red Correct order... The blood passes into the left atrium The blood re-enters the heart via the pulmonary vein The blood passes through the bicuspid valve and into the left ventricle The blood is pumped through the semi-lunar valve The blood leaves the heart via the aorta The blood travels to the lungs where it fills with oxygen and loses its carbon dioxide The blood passes out of the heart via the pulmonary artery The blood is pumped through the semi-lunar valve The blood passes through the tricuspid valve and into the right ventricle The blood passes into the right atrium The blood enters the heart from the body via the vena cava The blood travels around the body, depositing oxygen and collecting carbon dioxide Stand up behind your desk Complete the following workout; March on the spot for 30 secs Jump up and down 10 times Jog on the spot for 30 seconds Crouch down and stand up 5 times Run on the spot for 30 seconds What happens to your body?