* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Steps of Phagocytosis
Survey
Document related concepts
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
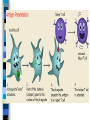
Phagocytosis
= basic tool of innate immune respons
phagocyting cells
steps of phagocytosis
Phagocyting Cells
neutrophile granulocytes
destroying of extracellular bacteria,
short lived cells, pus forming cells
Monocytes / macrophages
destroying of self cells and intratracellular
micoroorganism, long lived cells
presentation of antigen to T cells
dendritic cells presentation of antigen to T
cells
The granulocytes
often take the first stand during an infection.
They attack any invaders in large numbers,
and "eat" until they die.
The pus in an infected wound consists chiefly
of dead granulocytes.
The macrophages ("big eaters")
- start out as white blood cells called
monocytes. Monocytes that leave the blood
stream turn into macrophages.
- are slower to respond to invaders than the
granulocytes, but they are larger, live longer,
and have far greater capacities.
- play a key part in alerting the rest of the
immune system (adaptive immunity)
The dendritic cells
are "eater" cells and devour intruders, like the
granulocytes and the macrophages.
And like the macrophages, the dendritic cells help
with the activation of the rest of the immune
system.
They are also capable of filtering body fluids to clear
them of foreign organisms and particles.
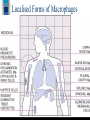
Localised Forms of Macrophages
Steps of Phagocytosis
migration to the site of inflammation
recognition of the antigen
ingestion
destroying of the pathogen
presentation of the antigen
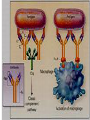
Migration to The Site of Inflammation
Neutrophils and monocytes:
in circulation 7 %
in bone marrow 93%
ratio is changed in inflammation
Migration to The Site of Inflammation
rolling along the vessel wall
contact between phagocyte and
endothelial cell = adhesion
passing through the vessel wall
(diapedesis, extravasation)
migration in tissue = chemotaxis
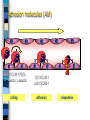
Adhesion molecules (AM)
a4/b1/VCAM-1 PSGL1/P-selectin L-selectin
rolling
CD18/ICAM-1
a4/b1/VCAM-1
adhesion
diapedesis
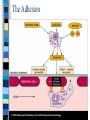
Contact of Phagocyte and Endothelium Adhesion Molecules
endothelium
phagocytes
selectins + sacharid structrures of neutrophil
(sialyl Lewis antigen) = rolling
ICAM-1 + β 2 integrins (CD 11/CD 18)
of neutrophils
VCAM-1 + β 1 integrins of monocytes
The Adhesion
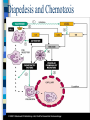
The Moving in Tissue = Chemotaxis
Receptors for chemotactic factors:
IL-8
C3a, C5a
leucotrien B4
platelet activating factor (PAF)
bacterial proteins (fMLP)
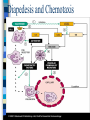
Diapedesis and Chemotaxis
Immune Recognition
PAMPs
pathogen associated molecular patterns
DAMPs
damage associated molecular patterns
PRRs
pattern recognition receptors of
phagocytes
PAMPs
pathogen associated molecular patterns
conserved in evolution
shared by a large group of infectious agents
clearly distinguishable from self pattern
Gram-negative
Gram-positive
Yeast
lipopolysacharide
lipoteichoic acid
cell wall mannans
PRRs (pattern recognition receptors)
of phagocytes
lectins = proteins able to bind carbohydrates
mannose and galactose receptor
toll-like receptors
TLR1 – TLR10
CD14 scavenger receptors for lipopolysacharides
OPSONISATION
= making tasty for the eater, „ spice“
receptors of phagocytes for
antibodies (binding Fc fragment)
complement C3
Diapedesis and Chemotaxis
The Ingestion
The adherence: PRR and PAMP
Pseudopods around the particle:
interaction of receptors and activating an
actin and myosin contractile system
Plasma membrane is completly around:
the vacuole = phagosome
phagosome + lysosom = phagolysosom
Steps of Phagocytosis
Microbicidal Mechanisms
oxygen independent:
antimicrobial proteins (defensins)
enzyms (cathepsin, lysozym, lactoferrin)
oxygen dependent:
catalyzed by NADPH oxidase:
NADPH + O2 = NADP + superoxide anion O2-,
reactive oxygen radicals
myeloperoxidase, halogenating system
nitric oxide
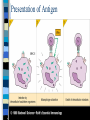
Presentation of The Antigen
fragments of an antigen bind to MHC
molecules on the surface of phagocyting cell
= antigen presenting cell (APC)
APC presents the antigens fragments
to T cells
T cells help B cells to produce specific
antibodies, activate specific cytotoxic T cells
cooperation between innate and adaptive
immunity
Presentation of Antigen
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=suCKm97y
vyk
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I9zSe0qm
XGw.