* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4_28_15-PBS-Day 8 - Kenwood Academy High School
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
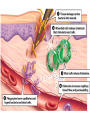
Do Now—4.28.15 What is the largest organ humans have? Do Now—4.28.15 What is the largest organ humans have? Skin Five points toward Summative Category Career Journal Extra Credit— Typed Hard Copy due Monday Complete a career journal for a microbiologist , lab technician, or an APPROVED profession. Unit 5: Infectious Diseases 5.1.6:Lines of Defense Objective SWBAT compare and contrast nonspecific and specific defense mechanisms. True or False True or False 1. Antibiotics can be used to treat a cold. 2. Doctors can check your lymph nodes to see if you are sick. 3. Vaccines can be used to prevent an infection. 4. Antibiotics contain antibodies. 5. Viruses are alive. 6. HIV can be cured. 7. The lymphatic system has over 500 structures. True or False True or False: T = 2, 3, 7. F = 1, 4. T/F = 5, 6. 1. Antibiotics can be used to treat a cold. 2. Doctors can check your lymph nodes to see if you are sick. 3. Vaccines can be used to prevent an infection. 4. Antibiotics contain antibodies. 5. Viruses are alive. 6. HIV can be cured. 7. The lymphatic system has over 500 structures. 5.1.6: Lines of Defense Terms Pathogen: infectious agent Terms Pathogen: infectious agent Antigen: substance that causes antibodies to be produced Terms Pathogen: infectious agent Antigen: substance that causes antibodies to be produced Antibody (Immunoglobulin): protein produced by B cells to inactivate an antigen (stop them from making the body sick). Lymphatic (immune) System The lymphatic (immune) system protects the body against pathogens. There are three basic lines of defense. 1) Nonspecific external barriers 2) Nonspecific internal barriers 3) Specific barriers Lymphatic (immune) System The nonspecific barrier does not have to recognize a particular invader to protect against it. Nonspecific External Barriers Nonspecific external barriers – Skin is a physical nonspecific external barrier that blocks pathogen entry and suppresses microbe growth. Nonspecific External Barriers Nonspecific external barriers – Skin is a physical nonspecific external barrier that blocks pathogen entry and suppresses microbe growth. – Nose hair/Mucus membranes are external mechanical barriers. Mucus traps pathogens and has antibacterial enzymes to kill pathogens. How do pathogens enter the body? How do pathogens enter the body? Breaks in the skin (cut / splinter / etc.) Mouth, ears, eyes, nose, genital, urinary, & anal openings. Nonspecific Internal Barriers Nonspecific internal barriers – WBC/Phagocytic Cells: ingest dead cells, cellular debris, and microbes by phagocytosis. (think of them like Pac Man) Nonspecific Internal Barriers Nonspecific internal barriers – Inflammation: attracts phagocytic cells and promotes blood flow and clotting. Histamine attracts WBCs, the cytokines released by the WBCs attract even more WBCs. The histamine causes tissue to be red, swollen, painful, and warm. Nonspecific Internal Barriers Nonspecific internal barriers – Inflammation: attracts phagocytic cells and promotes clotting. Histamine is produced by damaged cells. The histamine causes tissue to be red, swollen, painful, and warm. Specific Immune Response A specific immune response is when lymphocytes (B and T cells) respond to particular pathogens in the body. – Cell-mediated response (T cells) – Antibody-mediated response (B cells) Specific Immune Response: Cell-mediated response Cell-mediated response (T cells) – Macrophages present antigens to Helper T (CD8) cells, which causes activation of B cells and Cytotoxic (CD4/Killer) T cells. Cytotoxic T cells kills infected cells. Specific Immune Response: Antibody-mediated response The Helper T cell causes activation of the complementary B cell. B cells can also activate themselves. This B cell proliferates and differentiates into plasma B cells and Memory B cells. Specific Immune Response: Antibody-mediated response The Helper T cell causes activation of the complementary B cell. B cells can also activate themselves. This B cell proliferates and differentiates into plasma B cells and Memory B cells. Plasma B cells make antibodies. Memory B cells remember/recognize specific antigens in the future (mount faster response) Exit Slip In your own words, what is the difference between specific and nonspecific immunity? 5.1.6: Lines of Defense Homework None.