* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immune
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
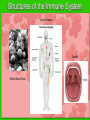
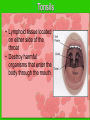
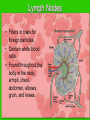
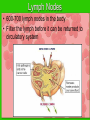
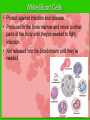
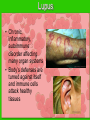
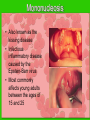
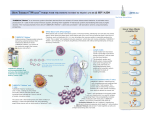
The IMMUNE System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Immune System • Provide immunity to the body by protecting against disease. • Identify and kill pathogens and tumor cells. • Produces white blood cells and antibodies. • Filters out organisms that cause disease. Structures of the Immune System http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/imagepages/9069.htm Structures of the Immune System Lymph Nodes Tonsils White Blood Cells Tonsils • Lymphoid tissue located on either side of the throat • Destroy harmful organisms that enter the body through the mouth Lymph Nodes • Filters or traps for foreign particles. • Contain white blood cells. • Found throughout the body in the neck, armpit, chest, abdomen, elbows, groin, and knees. Lymph Nodes • 600-700 lymph nodes in the body • Filter the lymph before it can be returned to circulatory system White Blood Cells • Protect against infection and disease. • Produced in the bone marrow and move to other parts of the body until they’re needed to fight infection. • Not released into the bloodstream until they’re needed. Structures of the Immune System Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell. There are B and T type lymphocytes. B cells produce antibodies. Antibodies attach to a specific antigen and make it easier for the immune cells to destroy the antigen. T cells attack antigens directly and help control the immune response. They also release chemicals, known as cytokines, which control the entire immune response. Diseases and Disorders Immune System HIV • Affects T cells within the immune system. • Attacks the RNA of the T cell, causing the T cell to alter its DNA structure to that of HIV. • Causes the T cells to replicate and create more HIV • When infected AIDS is the final stage of the HIV infection. AIDS Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome • Contagious disease comprising the immune system • Caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) • Capable of becoming multi-drug resistant • AIDS is the final stage of the HIV infection • Average incubation period for AIDS development is 10 years from point of infection • Characterized by “opportunistic infections” • There is no cure!! Lupus • Chronic, inflammatory, autoimmune disorder affecting many organ systems • Body’s defenses are turned against itself and immune cells attack healthy tissues Mononucleosis • Also known as the kissing disease • Infectious inflammatory disease caused by the Epstein-Barr virus • Most commonly affects young adults between the ages of 15 and 25 Careers • Microbiologist – research-oriented scientist • Epidemiologist – identify and track diseases • Ethicist – ethics in medicine or medical law and ethics in delivery of health care. Microbiologist • A microbiologist is a scientist who works in the field of biology. Microbiologists can be known under different names depending on the field of microbiology they specialize in. A medical microbiologist will specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of microbial diseases in patients. • Salary:$40,000/yr • Education: Bachelors degree in an area of specialty. Epidemiologist • Identify and track diseases as they occur in a group of people. Determine risk factors that make the disease more likely to occur and evaluate situations that may cause occupational exposure to toxic substances. • Salary: $40,000 + • Education: Minimum of bachelors degree, Masters degree is recommended. Ethicist • Offers guidance to patients, their familes, professional staff on ethical, legal and policy issues and concerns. Provides guidance to institutional ethics committees to follow policy and educational review activites. • Salary: $70,000/yr • Education: Masters or Doctorate related to health ethics and at least 5 years of experience in the field.