* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download T cell
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
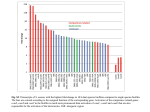
NEGATIVE REGULATION OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM NEGATIVE REGULATION IN THE IMMUNE SYSTEM 1. Decrease of antigen concentration in the course of the immune response 2. Inhibition of B lymphocyte activation - antibody feedback • Cross linking of BCR with FcRIIB (CD32) by antigen-antibody complex • ITIM-induced negative signaling of B cell activation - phosphatases • B cells without T cell help are excluded from follicles 3. Death of activated T lymphocytes • Passive cell death mediated by the shortage in survival factors (cytokines) • Activation induced FasL expression sensitizes activated T cells for Fas• mediated apoptosis (AICD) • Activation induced cell death (AICD) is induced by repeated antigenic stimulation 4. Inhibition T lymphocyte activation • Anergy of CD4+ T lymphocytes • Late in the immune response activated T cells express CTLA-4, the ligand of B7 4. Suppression by regulatory T lymphocytes • Counter regulation of Th1 and Th2 cytokines • Production of suppressive cytokines • IL-10 inhibits APC function such as IL-12 secretion and B7 expression • TGF inhibits T-cell proliferation • IL-4 inhibits IFN-mediated functions • IL-10 and TGF inhibit macrophage activation NEGATIVE REGULATION OF IMMUNE RESPONSES AICD DIFFERENTIATION Naive lymphocytes Memory Primary effectors Number of antigen specific cells Secondary effectors EXPANSION AICD MEMORY 5 10 15 20 25 30 Days IMMUNOGLOBULIN BINDING Fc RECEPTORS FcγRI (CD64) FcγRII (CD32) IIa Ib IIc IIb1 IIb2/IIb3 tetramer FcεRII Ca 2+ trimer Ca 2+ Ca 2+ SS SS -S-S- SS SS SS SS SS SS SS SS SS SS Iγ-γ SS SS Ia FcεRI -S-S- -S-S- -S-S- SS SS ITAM α FcγRIII (CD16) SS SS SS SS SECRETORY PIECE SS SS γ-γ α SS IIIb SS SS IIIa poli-Ig re ceptor SS SS α γ-γ FcRI SS IIIaζ-ζ IIIaζ-γ IIIaγ-γ IIIaβ β γ-γ SS ITIM SS ITAM SS ITAM ITAM IgG Fc receptors Ig supergene family, MIRR Activating receptor ITAM Expression Inhibitory receptor ITIM Expression Fc receptorok Ig supergene family BCR* B cell TCR,* CD3* T cell FcRIa (CD64) FcRI* Macrophage, DC (internalization) FcRIIa (CD32) Macrophage, DC (internalization) FcRIIIa (CD16) FcRI* vagy * NK cell (ADCC) FcRI, FcRI* Mast cell (ADCC) FcRIIb (CD32) B cell FcRIIb (CD23b) FcRIIa (CD23a) B cell Human KAR Human KIR NK and T cell C-type lectin MHC I receptorok Ig supergene family C-típusú lektin Egér KIR Human NKG2C/D NK and regulatory T cell Human NKG2A/B NK and regulatory T cell BCR CD22 B cell CD28 CTLA-4 T cell Other receptors MIRR Multisubunit Immune Recognition Receptors The ligand binding and signal transducing subunits are separated, they co-localize in membrane microdomains. NEGATIVE REGULATION OF B LYMPHOCYTES BY IMMUNE COMPLEXES ITAM FcRIIb ITIM Costimulatory molecules also associate with inhibitory receptors T cell Signal 1 + 2 2 Activated T cell -- -- CD28/CTLA-4 CD28 B7 B7 CD28 cross linked by B7 Co-stimulation induces CTLA-4 Cross-linking of CTLA-4 by B7 inhibits co-stimulation and inhibits T cell activation CTLA-4 binds CD28 with a higher affinity than B7 molecules The lack of signal 2 to the T cell shuts down the T cell response. NEGATIVE REGULATION OF T CELL ACTIVATION BY CTLA-4 T APC CD28 B7 CTLA-4 LATE EXPRESSION HIGHER AFFINITY TO B7 THAN CD28 THE ROLE OF CD4+ T CELLS IN APOPTOSIS 4+ CD Th1 B CD4+ Th1 Fas L APC F as C D 8+ Tc T CELL HOMEOSTASIS SHUT OFF IMMUNE RESPONSES REGULATORY T CELLS REGULATORY T CELLS MARKERS OF THYMUS DERIVED NATURAL Treg CELLS CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ GITR CTLA4 B7 ligand Treg FoxP3 CD25 IL-2Rα CD127 IL-7Rα ↓ Treg differentiation, maintenance, function Transcription factor – many target genes Itself is not sufficient to confer suppressive function A TGFβ does not induce regulatory function FUNCTIONS OF REGULATORY T CELLS •Maintenance of peripheral tolerance •Prevention of autoimmunity •Limiting inflammatory processes (asthma, inflammatory bowel diseases) •Inhibit protection against infectious diseases •Limit immune responses to tumors MECHANISM Intrinsic and extrinsic regulation Various inhibitory mechanisms Cell contacts – Cytokines Interaction with the target effector T cells REGULATORY FUNCTION OF REGULATORY T LYMPHOCYTES Inhibitory cytokines Cytolysis TGFβ IL-10 IL-35 Metabolic dysregulation Descreased cytokine production (IL-2) Adenosin around the cell cAMP transfer Inhibition of dendritic cell maturation Indolamin2,3-dioxigenase LAG-3 – CD4 homolog Treg : effektor T cell = 1 : 8 Treg : DC = 1 : 0,8 THE ROLE OF IL-35 IN THE FUNCTION OF REGULATORY T CELLS Initial T cell activation Sensed by Treg cells Increased suppressive mechanisms •The molecular patterns of activated Treg cells are different in the presence and absence of effector cells •The expression of EBI3 and IL-12α/p35 (IL-35) subunits is increased in the presence of effector T cells •Treg cells in contact with effector cell act also on effector cells out of contact through IL-35 Induced capability, the effector cell is involved NOT ONLY A FUNCTION REGULATORY CELLS ARE ABLE TO CONTROL LOW LEVEL ACTIVATION