* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AUTOIMMUNITY
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatoid arthritis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
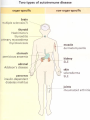
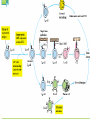
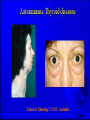
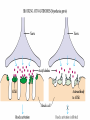
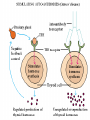
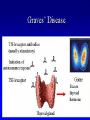
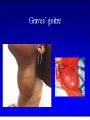
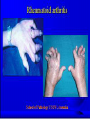
AUTOIMMUNITY Dr. Anand Kumar & Dr. R.. A. Siddique N.D.R.I., Karnal (Haryana) India, 132001 [email protected] Self/Non-self Discrimination Autoimmunity is a problem of self/non-self discrimination. Autoimmunity • 5 % to 7% adult affected. • Two third women. • More than 40 human diseases autoimmune in origin. AUTOIMMUNITY & LEFTHANDEDNESS • LEFT handed individuals more affected. • 11% of left handed & 4% of right handed. • Reasons for this are obscure. • left-handedness & immune malfunction may both result from abnormal endocrine function in fetal life. Effects of autoimmunity 1) Tissue destruction Diabetes: CTLs destroy insulin-producing b-cells in pancreas 2) Antibodies block normal function Myasthenia gravis: Ab binds acetylcholine receptors 3) Antibodies stimulate inappropriate function Graves’ disease: Ab binds TSH receptor Mimics thyroid-stimulating hormone Activates unregulated thyroid hormone production 4) Antigen-antibody complexes affect function Rheumatoid arthritis: IgM specific for Fc portion of IgG IgM-IgG complexes deposited in joints inflammation Causes of autoimmunity • • • • • • • • 1) Release of sequestered Ag Smoking can trigger Goodpasture’s syndrome Alveolar basement membrane normally not exposed to immune system Smoking damages alveoli, exposes collagen Anti-collagen Ag damages lung and kidney Anti-sperm Ab produced in some men after vasectomy Injection of myelin basic protein (MBP) produces MSlike EAE • in mice • May be triggered by injury or infection Causes of autoimmunity • 2) Immune stimulation • Microbial infection stimulates APCs carrying self Ag • High level of APCs with “second signal” breaks anergy Mechanisms of autoimmunity • Ag released from hidden location. • Antigen generated by molecular changes. • Molecular mimicry. • Alteration in Ag processing. • Infection. • Genetic factors. Mechanisms of autoimmunity • Lymphocytes abnormalities. • Failure of central tolerance. • Overcome of peripheral tolerance. • Polyclonal lymphocytes activation. Ag related from hidden location Many self Ag are found in hidden location eg. C N S ,TESTES ,EYE (CORNEA) organ damage Hidden Ag released Reaches blood stream Encounter Ag sensitive cells Stimulate autoimmunity Antigen generated by molecular changes • Development of completely new epitopes on normal protein. eg RF immuno conglutinine. Mech of formation of RF : Ab + Ag new epitopes exposed on Fc region of Ab Stimulate the formation of Rf Establishment of disease like rheumatiod artheritis and SLE Molecular mimicry • Sharing of epitopes between an infectious agent and its host. • Antibodies directed against the infectious agents starts reacting with normal self Ag. • Triggers autoimmunity. Alteration in Ag processing • A T cell may fail to develop tolerance to an self Ag simply because it is not efficiently procured. • If something happens to improve the processing, an autoimmune disease may be triggered. • This usually happens at the site of inflamation resulting in modified Ab. • Eg. Thyrotoxicosis , diabetese. Infection • Here autoimmunity is not due to infectious agent itself ,but results from dis regulation of host immune response by the microbes. This may be due to : • Polyclonal lymphocyte activation. • inhanced stimulation of co stimulator. • Alteration of self Ag(cross reactive neo-Ag) GENETIC FACTORS • The important genes that regulate the development of autoimmunity are located within MHC. • MHC have got critical role in maturation of T cell & induction of IR . • MHC ll genes are directly responsible for auto antigen processing and presentation. • The structure of Ag binding groove will determine , if specific Ag will trigger an AU response. • Eg. Diabetes mellitus in dog: DLA-A3, A7, A10 and DLA-B4 SLE: DLA- A7 POLYARTHRITIS: DLA- A7 Lymphocytes abnormalities • Primary abnormalities either in B cell or T cell. • Since these cells are critical regulators of all IR. • MHC presentation of all antigenic peptide to these cells will be defective, in case the cells are abnormal. • Abnormalities in lymphocytes could affect any one of the mechanism that normally maintains self tolerance. Failure of central tolerence Inside primary lymphoid organ; positive selection negative selection (Deletion of self reacting T cells in thymus apoptosis). Failure of central tolerance starts AU diseases. POLYCLONAL LYMPHOCYTE ACTIVATION • Stimulation of non deleted self reacting lymphocytes. These are activated by some activators• LPSPOLYCLONAL B CELL ACTIVATOR • BACTERIAL SUPER ANTIGENPOLYCLONAL T CELL ACTIVATOR Damage to immunologically privileged sites can lead to autoimmunity Rheumatiod Arthritis • Auto-immune disorder which results in inflammation of the synovial lining of the joint and cartilage destruction. • This result in loss of function. • Affects 1% of adults. Treatment for autoimmunity • • • • • • • Immunosuppression (e.g., prednisone, cyclosporin A) Removal of thymus (some MG patients) Plasmapheresis (remove Ab-Ag complexes) T-cell vaccination (activate suppressing T cells??) Block MHC with similar peptide anti-CD4 monoclonal Ab anti-IL2R monoclonal Ab