* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Airgas template
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
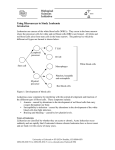
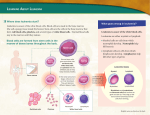
Essentials of Pathophysiology CHAPTER 11 DISORDERS OF WHITE BLOOD CELLS AND LYMPHOID TISSUES PRE LECTURE QUIZ (TRUE/FALSE) T F F T F White blood cells (granulocytes, monocytes, and lymphocytes) are formed in the bone marrow. The life span of white blood cells is relatively long, so constant renewal is not necessary to maintain normal blood levels. In neutropenia, all of the cell lines are affected, resulting in anemia, thrombocytopenia, and agranulocytosis. Infectious mononucleosis is a self-limiting disorder caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). Non-Hodgkin is a form of lymphoma that is associated with the presence of an abnormal cell called a Reed-Sternberg cell. PRE LECTURE QUIZ Acute Clinical manifestations of acute leukemia include petechiae, ecchymosis, gingival bleeding, and epistaxis, as a result of a decreased ________________________________ level. More children are stricken with ____________________ than with any other form of cancer, and it is the leading cause of death in children between the ages of 1 and 14 years. Cell Leukemia Philadelphia The ________________ leukemias have a sudden and stormy onset with symptoms of depressed bone marrow function (Ph) (anemia, fatigue, bleeding, and infections). thrombocyte/ The leukemias are classified according to their predominant ________________________ type. platelet Chronic myelogenous leukemia is associated with the presence of the _________________________ chromosome, arising from a reciprocal translocation between the long arm of chromosome 22 and the long arm of chromosome 9. DEVELOPMENTAL STAGES OF BLOOD CELLS WHITE BLOOD CELLS WHITE BLOOD CELLS OR LEUKOCYTES Granulocytes Neutrophils: primary pathogen-fighting cells Eosinophils: help control allergic responses; fight parasites Basophils: release heparin, histamine, and other inflammatory mediators WHITE BLOOD CELLS OR LEUKOCYTES (CONT.) Lymphocytes B cells: create antibodies T cells: control immune response; cell-mediated immunity Natural killer cells: kill antigenic cells Monocytes/macrophages: antigen-presenting cells; create inflammatory mediators QUESTION Which type of leukocyte works the hardest when you receive a vaccination? a. Eosinophil b. Basophil c. B-lymphocyte d. Neutrophil ANSWER B-lymphocyte A vaccination introduces antigens, causing your body to create antibodies to fight the antigens. B-lymphocytes create those antibodies. Eosinophils and basophils are part of the allergic/immune response; neutrophils work to fight infections. c. Cell differentiation MYELOID TREE common myeloid stem cells committed precursor cells platelets erythrocytes monocytes and granular leukocytes LYMPHOID TREE common lymphoid stem cells committed precursor cells T lymphocytes B lymphocytes natural killer cells Multipotent stem cells common lymphoid stem cells common myeloid stem cells committed precursor cells committed precursor cells T lymphocytes B lymphocytes natural killer cells platelets erythrocytes monocytes and granular leukocytes QUESTION Which type of leukocyte is created in the bone marrow (myeloid)? a. Eosinophil b. Basophil c. Neutrophil d. All of the above ANSWER All of the above Granular leukocytes are created in the bone marrow; eosinophils, basophils, and neutrophils are all granular leukocytes. d. SCENARIO: A man has cancer and is being given radiation therapy… His doctor has prescribed several drugs: Question: Why have the following drugs been prescribed? Erythropoietin Granulocyte-monocyte factor Thrombopoietin colony-stimulating WHITE BLOOD CELL COUNT White blood cell counts vary between species The denser the population, the more neutrophils The more sexual partners, the more eosinophils Question: What can you infer about diseases in these populations? WHITE BLOOD CELL DEFICIENCIES Leukopenia Neutropenia (agranulocytosis) Aplastic anemia Infectious mononucleosis HIV QUESTION Patients with HIV are immunocompromised. Which type of leukocyte is the best indicator of immune function? a. Neutrophil b. Eosinophil c. T-lymphocyte d. Monocyte ANSWER T-lymphocyte Because T-lymphocytes direct the immune response, they are used to evaluate immune function. Patients with HIV are usually treated pharmacologically when their T-cell counts drop below 350 cells/mm3; they are considered to have AIDS when their T-cell counts drops to 200 cells/mm3. c. LEUKEMIAS Malignant neoplasms of hematopoietic stem cells In bone marrow Create abnormal white blood cells: 2 types of leukemia Lymphocytic Myelogenous Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) AML MYELOID BLASTS Bone marrow aspirate showing acute myeloid leukemia. Several blasts have Auer rods. Auer rods are clumps of granular material that form elongated needles seen in the cytoplasm of leukemic blasts. MYELOCYTIC LEUKEMIAS Mutation of myeloid cell line Overproduction of abnormal monocytes or granulocytes Production of other cell types decreases Multipotent stem cells common lymphoid stem cells mutation neoplastic inmyeloid myeloid stem cells neoplastic committed precursor cells abnormal monocytes or granular leukocytes LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIAS Mutation of lymphoid cell line Overproduction of abnormal immune cells Production of other cell types decreases Multipotent stem cells mutation neoplasticin lymphoid stem cells common myeloid stem cells neoplastic committed precursor cells neoplastic abnormal B or T lymphocytes or natural Natural killer Killercells cells LEUKEMIAS What is the difference between: Acute vs. chronic Lymphocytic vs. myelogenous AML GENE TRANSLOCATION LEUKEMIAS AFFECT BONE MARROW ACTIVITY Question: How would this cause: Bone pain and risk of fractures? Anemia? Thrombocytopenia? Immune suppression? QUESTION What signs and symptoms will result when…? Abnormal WBCs are produced and they… Release inflammatory mediators Infiltrate peripheral lymphoid organs Increase blood viscosity Create waste products SCENARIO: A child develops night sweats and nosebleeds… He appears pale, weak, and fatigued Cervical lymph nodes are enlarged Blast count is elevated After chemotherapy, he develops hyperkalemia. Question: Why did this happen? ANSWER When there is a breakdown or destruction of cells, the electrolyte potassium moves from inside of the cell to outside of the cell wall. This shift of potassium outside of the cells causes hyperkalemia. Lymphoma vs. Leukemia or Dyscrasias WBCs are formed and differentiate in the bone marrow They travel to the lymphoid organs to mature and develop Lymph node Neoplasms arising here cause leukemias or plasma cell dyscrasias Neoplasms arising here are lymphomas LYMPHOMAS Hodgkin lymphoma Malignant B cells invade lymphoid organs Non-Hodgkin lymphoma B cell T cell MYELOMA Abnormal B cells Can form tumors dyscrasias - a malfunction or abnormal condition, esp. an imbalance of the constituents of the blood. Produce abnormal antibodies Immune depression Proteins increase blood viscosity Infiltrate organs Proliferation of osteoclasts Break down bone QUESTION True or False: Hodgkin lymphoma has a better prognosis than non-Hodgkin lymphoma. ANSWER True Non-Hodgkin lymphoma originates from malignancies in both T- and B-lymphocytes, where Hodgkin malignancies originate in Bcells (a specific type called the Reed-Sternberg cell). Therefore, more immune function is lost in non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and the prognosis is not as good.