* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Learning - Hale
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
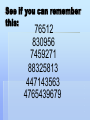
Learning HSP3M Conditioned Learning Definition: Acquiring patters of behaviour in the presence of an environmental stimulus i.e. learning to respond to a particular stimulus in a particular way Two types: Classical Conditioning Operating Conditioning Classical Conditioning Key figure: Ivan Pavlov Pavlov’s dog Sounded bell right before giving the dog food Initially, the food caused the dogs to salivate Eventually the dogs salivated at the sound of the bell alone Classical Conditioning An unconditioned stimulus (US) is paired with a conditioned stimulus (CS) to turn an unconditioned response (UR) to a conditioned response (CR) 1. US UR 2. US + CS UR 3. CS CR Operant Conditioning Key figure: BF Skinner Skinner realized that most behaviour is not the result of the pairing of unrelated stimuli Skinner put a rat in a cage that had a bar that, when pushed, would drop a food pellet into the cage The rat randomly pushed the bar and got food The next time it pushed the bar, it got more food Eventually it pushed the bar constantly, knowing it would get food Operant Conditioning Using rewards to reinforce behaviours, and punishments to discourage them Positive reinforcement: an event/condition that increases the likelihood that a certain behaviour will reoccur Negative reinforcement: an event/condition that decreases the likelihood that a certain behaviour will reoccur Operant Conditioning Which do you think is more effective, rewards, or punishment? Observational Learning Behaviour that is not conditioned, but repeated based on seeing someone else do it Think about playing sports, driving a car etc. Most of our early skills are learned through observation See “Imitating Violence” on p. 57 Impact of violence on TV/video games? Observational Learning 1. Attention: Paying attention to the behaviour of others 2. Retention: Remembering what you’ve observed (how they did it, the result) 3. Reproduction: Trying it yourself (practicing) 4. Motivation: Believing that the skill is useful enough to practice (can be internal or external) Memory See if you can remember this: 76512 830956 7459271 88325813 447143563 4765439679 . . . . . . Draw the image on a loonie from memory Can you remember the names of all your teachers from grade school? Memory The capacity to acquire, retain, and recall knowledge and skills Episodic memory: remembering things from the past Semantic memory: knowledge of how the world works Procedural memory: knowing how to do things 3 Levels of Memory Sensory Memory Based on 5 senses Only recorded for a few seconds – once you’ve recorded the necessary information, the sensory memory fades Examples: Taste of sandwich in your mouth Sight of a squirrel crossing the road Feel of chair against your back 3 Levels of Memory Short-term memory What’s going on in your conscious mind right now Holds information for 15-20 seconds Most people can remember about 7 separate, unorganized items in short term memory Can work with more if you organize it into groups Example: someone tells you their phone number and you punch it into your cell phone 3 Levels of Memory Long-term Memory Which is easier to remember, the name of a friend, or the name of the waiter at the last restaurant you dined at? If it’s important to you, you’ll remember it Long-term memory is unlimited, but we not always be able to recall the information 3 Levels of Memory Tricks to improving your long term memory? Ascribe personal meaning Mnemonic device Recall items regularly Organization