* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classical Conditioning
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
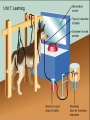
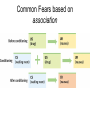
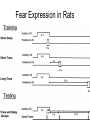
Unit 7: Learning Behaviorism • Belief that behavior is learned – genetics has little to do with it. • “nurture-only” belief, mainstream1960s and 70s. • Behaviorists believed learning done through associations. • Behaviorists want psychology to be a science: – observable, testable and measurable. Attributes of Learning A. Learning = relatively permanent change in behavior or knowledge as a result of experience B. Distinction between learning and performance • Performance is an exhibited behavior • Learning can be inferred from performance, but performance is not always an accurate measure of learning C. Learning is adaptive – Unlike most species whose behavior and bodies have adapted to a certain environment – humans have the capacity to learn – Increase in speed of adaptation in comparison • Learning and thinking (cognition) have allowed us to adapt to all environments on earth, without our bodies changing. Classical Conditioning • Ivan Pavlov: Classical Conditioning. http://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=nE8pFWP5QDM Definitions 1. Classical conditioning: learning that takes place when originally neutral stimulus comes to produce a conditioned response because of its association with an unconditioned stimulus • In other words – CREATING A REFLEX 2. An unconditioned stimulus (UCS or US) produces an unconditioned response (UCR or UR), even in the absence of previous training 3. A conditioned stimulus (CS) is a stimulus that has come to elicit a conditioned response (CR) because the organism associates the conditioned stimulus with the unconditioned stimulus - Initially called the “neutral stimulus” So let’s go back to Jaws… Pavlov’s Classical Conditioning: Pavlovian Response or “Psychic Reflex” • accidental psychologist: studying digestion initially • theory links to emotion, temperament, neuroses, and language Pavlov’s Experiment Unconditioned vs. Conditioned Responses • In Pavlov’s demonstration UR = CR – Salivation • Although UR and CR consist of same behavior, there are subtle differences – CR usually weaker or less intense • Sometimes UR and CR are different but related – Animal given a shock, UR = pain, CR = fear of imminent pain Conditioned Reflex • Classically conditioned responses described as reflexes – Involuntary and automatic Taste aversions? Trials • How long does it take to learn something? Classical Conditioning Applications 1. Conditioned Fear and Anxiety • • Phobias Irrational fear due to classical conditioning • • Fear of dentist drill Careful though – susceptibility of irrational fear is mostly based on genetics… how? Common Fears based on association 2. Emotional Responses – Arousal • Smell of first love’s cologne/perfume 3. Physiological Responses • Sexual arousal in quails – Conditioned to become aroused by nonsexual stimuli – Conditioned to elicit increased sperm release – Fetishes for inanimate objects • Difficult to test connections to human sexual fetishes 4. Evaluative Conditioning of Attitudes (evaluative conditioning) • Changes in the liking of a stimulus that result from pairing that stimulus with other positive or negative stimuli – MARKETING – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pfvq2Gf6U E8 Volunteers? B. Acquisition: initial stage of learning something 1. Involves repeated pairings of the CS and the UCS/US 2. Acquisition Paradigms (patterns) • What are the different ways in which the initial learning can take place? a. Trace Conditioning – – – – – CS is presented and terminated BEFORE presentation of the UCS/US Conditioning often effective when the interval BETWEEN presentation of the CS the UCS/US is about a half second Fear studies; dependent on usage of hippocampus http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PsGjh6ul7mE b. Delay Conditioning – when CS is presented and continues at least until the UCS/US is presented – Often times paired with trace conditioning in studies – Hippocampus-independent – Fear expression Fear Expression in Rats c. Simultaneous Conditioning – Occurs when CS and the UCS/US are presented and terminated at the same time – Anti-smoking ads d. Backward conditioning – Occurs when the UCS/US is presented before the CS – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fT6IWAIf580 e. Temporal conditioning – Occurs when the nominal CS is a fixed period of time between presentations of the UCS/US – Combined with trace conditioning based on a period of time • i.e. dog starts to salivate at 7:59am because s/he is fed at 8am everyday C. Extinction 1. A procedure that leads to gradual weakening and eventual disappearance of CR • Involves repeatedly presenting CS without pairing it with UCS/US D. Spontaneous Recovery 1. Occurs when previously extinguished CR suddenly reappears after a period of training 2. Renewal effect • • • If a response is extinguished in a different environment than where it was acquired, the extinguished response will reappear if the animal is returned to the original environment where the acquisition took place Proves that extinction is a suppression not an erasure (unlearning) Explains drug abuse and relapse and difficulty getting rid of phobias permanently









































![Classical Conditioning (1) [Autosaved]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001671088_1-6c0ba8a520e4ded2782df309ad9ed8fa-150x150.png)


