* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint Notes from 2014 - John Brown, Election of 1860, and
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Fort Pulaski wikipedia , lookup
Battle of New Bern wikipedia , lookup
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hatteras Inlet Batteries wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Galvanized Yankees wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Henry wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Coast Theater of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Port Royal wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Fort Sumter wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
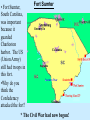
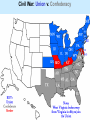
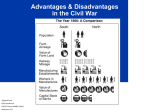
John Brown’s Raid: • In 1859, John Brown and his followers seized a federal arsenal in Harpers Ferry, Virginia. What is an arsenal? John Brown in August, 1859. Engine house at Harpers Ferry; aka John Brown’s Fort Inside the engine house at Harper’s Ferry Interior view of the engine house at Harpers Ferry during the siege. • Brown was caught and sentenced to death by hanging. Brown as a wounded prisoner after his capture. Brown being carried from court to prison. Last Moments of John Brown (painting by Thomas Hovenden) Do you think the artist was from the North or the South? Why? John Brown painting at Harper's Ferry "Now, if it is deemed necessary that I should forfeit my life for the furtherance of the ends of justice, and mingle my blood further with the blood of millions in this slave country whose rights are disregarded by wicked, cruel, and unjust enactments, I say, let it be done." --John Brown, statement at his sentencing on Nov. 2, 1859 The hanging of John Brown. "[John Brown is] that new saint, than whom none purer or more brave was ever led by love of men into conflict and death,--the new saint awaiting his martyrdom, and who, if he shall suffer, will make the gallows glorious like the cross." --Ralph Waldo Emerson, from his lecture "Courage," delivered in Boston on Nov. 8, 1859 HERO or VILLAIN “A house divided against itself cannot stand.” Emergence of Abraham Lincoln Republican Party – (new party) political party formed united under the belief that “no man can own another man...that slavery must be prohibited in the territories…that all new states must be free states…that the rights of our colored citizens…must be protected.” Lincoln- Douglas Debates: 1858 • Lincoln – the challenger – – – decries “Southern plot” to extend slavery promises to work for slavery’s extinction casts slavery as a moral problem, not just political • Douglas – the incumbent (already a senator) – accuses Lincoln of favoring equality • Lincoln loses election, gains national reputation “THE FIGHT MUST GO ON.” Election of 1860: Main Candidates Abraham Lincoln (Republican) John Breckinridge (Southern Democrat) Stephen Douglas (Northern Democrat) John Bell (Constitutional Union) * Lincoln won the election. Election Results • Lincoln wins with just 40% of the votes • 10 southern states did not put his name on the ballot • The South realizes that they have no power left in the government and that ending slavery would be a goal of the new president. Possibility of secession. • A Senate committee was formed to work out a compromise and save the Union Lincoln’s View on Slavery December 20, 1860 Interview with Lincoln • Promised not to interfere with slavery in the South. • He would support the enforcement of the Fugitive Slave Law. • Under no circumstance would he allow slavery to spread into the new territories. Secession: • In response to Lincoln’s victory, the southern states seceded from the Union, (the same day as his interview) forming the Confederate States of America (or the Confederacy). Original Confederate flag Eventual Confederate flag • Jefferson Davis was named the President of the Confederacy. Lincoln’s Inaugural Address “In your hands, my dissatisfied fellow countrymen, and not mine, are eth momentous issues of civil war. The Government will not assail (attack) you. You can have no conflict without being yourselves the aggressors…We are not enemies, but friends. We must not be enemies. Though passion may have strained, it must not break our bonds of affection.” • Fort Sumter, South Carolina, was important because it guarded Charleston harbor. The US (Union Army) still had troops in this fort. •Why do you think the Confederacy attacked the fort? Fort Sumter * The Civil War had now begun! Pvt. Edmund Ruffin, Confederate soldier who fired the first shot against Fort Sumter Maj. Robert Anderson, defender of Fort Sumter Bombardment of Fort Sumter, Charleston Harbor 12 and 13, 1861 April Fort Sumter, S.C., April 14, 1861, under the Confederate flag. Reaction to Fort Sumter Lincoln’s Response -75,000 Volunteers and a blockade of all Southern ports Both sides prepare for war Civil War: Union v. Confederacy