* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Plants: Evolution, Characteristics and Life Cycle
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
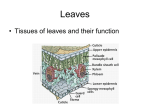
Plant Functions BIOL 1407 Essential Nutrients • Chemicals that organism cannot produce • Must be acquired from environment • Required to complete life cycle • Photo Credit: BIOL 1407 Student, Austin Nature Center, Fall 2006 Macronutrients • Large quantities – – – – – – – – – Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Sulfur Phosphorus Potassium Calcium Magnesium Zea mays Vascular Bundle (Orange = Sclerenchyma) Photo Credit: Barnading, 2002, Wikimedia Commons Micronutrients • Tiny quantities • Cofactors or components of enzyme systems Source of Plant Nutrients • Inorganic Compounds – Soil – Air Transport Systems • Why are they necessary? Types of Transport • Cell Transport – Across membrane • Short-distance – Diffusion from cell to cell • Long-distance – Bulk Flow – Down pressure gradients Absorption of Water & Minerals • From soil (most) • Absorption – Diffusion – Osmosis – Facilitated Diffusion – Active Transport Mineral Uptake: Cation Exchange • Cations firmly bound to soil particles • Roots secrete H+ – Directly by H+ pump – Indirectly by cellular respiration Short-Distance Transport • Lateral Transport – Symplast Pathway – Apoplast Pathway – Transmembrane Pathway Short-Distance Transport in Roots Long-Distance Transport • Xylem – Water – Minerals • Phloem – Organic compounds Xylem Xylem Transport • Root Pressure • Cohesion and Adhesion of Water in Xylem tubes • Transpiration Root Pressure • Loading of water and minerals into xylem vessels hydrostatic pressure in stele Cohesion & Adhesion Transpiration • Evaporation of water from plant surfaces • Mainly through leaf stomata Transpiration Pull Shoot Gas Exchange • Leaves – Cuticle – Stomata – Opening – Guard Cells – Regulate Gas Exchange • Stem – Lenticels • Photo Credit of Lenticels: Sten Porse, 2007, Wikimedia Commons Root Gas Exchange • No cuticle • No stomata Phloem Transport • Sugar Sources • Sugar Sinks Phloem Cells Lateral Transport of Sugars Apoplast Sieve tube element or companion cell Phloem Transport Plant Video • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J1PqUB 7Tu3Y The End Unless otherwise specified, all images in this presentation came from: Campbell, et al. 2008. Biology, 8th ed. Pearson Benjamin Cummings.