* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transport in Plants Lesson 10 Biology 10
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
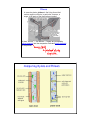
Transport in Plants Lesson 10 Biology 10 Objective: You will be able to -identify the xylem and phloem in plants -describe their function Xylem The xylem transports water and soluble mineral nutrients from the roots throughout the plant. It is also used to replace water lost during transpiration and photosynthesis. The transport is passive.the most important cause of xylem flow is the evaporation of water from the surfaces of mesophyll cells to the atmosphere. This flow is called transpirational pull. Xylem Vessels Xylem vessels are a long straight chain made of tough long dead cells known as vessel elements. The cells are arranged end to end and the cell walls which would normally surround the whole cell dissolve where ever they are touching another cell wall. Phloem In vascular plants, phloem is the living tissue that carries organic nutrients, in particular, sucrose, a sugar, to all parts of the plant where needed. At their "source" — the leaves — sugars are pumped by active transport into the companion cells and sieve elements of the phloem. Comparing Xylem and Phloem Transpiration-cohesion-tension 1. Water is constantly lost through transpiration from the leaf (stomata). 2. When one water molecule is lost another is pulled along by the processes of cohesion and tension. Cohesion: the attraction (sticking together) of different substances. Adhesion: the attraction (sticking together) of the same substance. Water forms drops because of this! 3. Transpiration pull, utilizing capillary action and the inherent surface tension of water, is the primary mechanism of water movement in plants. Guard Cells and Transpiration Read page of notes, use textbook and label diagram . (text p.309) Assignment Read p. 315-322 Do Check and reflect #1-8