* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Transport and Tropisms
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
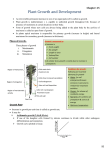
Plant Transport • Water Transport – 1. Enters root by osmosis – 2. Passes through cortex (parenchyma) tissue by osmosis – 3. Passes through endodermis • One way only • Combination of active transport and osmosis Plant Transport • Water Transport (cont) 4. Enters xylem • Cohesion– The attraction of water molecules to each other • Transpiration– The evaporation of water from the leaves of plants Plant Transport • Water Transport (cont) – 5. Transpiration Pull• The force that pulls water upward. • Cohesion holds the water column together as it moves upward through the xylem Plant Transport • Food Transport – Requires energy (active transport) – Translocation• Movement of food through the phloem – Pressure Flow Hypothesis (source-sink) • Food moves from an area of high pressure to low pressure Plant Transport • Food transport – High Pressure (Source)• Could be leaves when food is formed • Could be areas of food storage (root, stem, etc) – Low Pressure (Sink)• Could be where food is used for growth. • Could be where food is stored. Plant Motions • Auxins– Plant hormones • • – Stimulate or inhibit cells to grow Depends on the target organ Stem growth• – Auxins stimulate stem cell growth Root growth• Auxins inhibit root cell growth Plant Motions • Tropism– Response of a plant to environmental stimuli – Positive• Respond toward the stimulus – Negative• Respond away from the stimulus Plant Motions • Phototropism– Response of plants to light • Stem- positive Plant Motions • Gravitropism or geotropism– Response of plants to gravity • Stem- negative • Root- positive Plant Motions • Thigmotropism– Response of plants to touch • Tendril- positive Flowering • Photoperiodicity– • Response of flowering plants to different light conditions Short day plants– – Flower when time exposed to light is short ex. chrysanthemums & poinsettias Flowering • Long day plants– Flower when the amount of time exposed to light is long – ex. clover, petunias, & hollyhocks Flowering • Day-neutral plants– Length of light has no effect on flowering – ex. corn & tomato • Actually the amount of darkness, not light, that stimulates these plants