* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dr. Emiko Furusato - Midatlanticpas.org
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
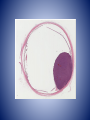
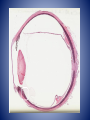
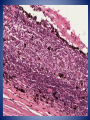
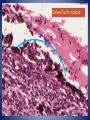
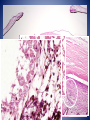
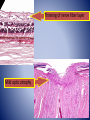
• Diagnosis – Chronic glaucoma with secondary angle closure following central retinal vein occlusion with hemorrhagic infarction of retina and neovascularization of iris. – Disciform macular degeneration Choroid Cases Case 8 Case History • • • • 41 yo male; Shadow over his left eye for 6M IOP : normal, Vision: 20/20 OD, and 20/25 OS. Left fundus revealed a large grayish yellow mushroom–like mass that elevated the retina superonasally. Case History • Tumor contained very little pigment and was not completely opaque on transillumination. • Visual field test revealed a scotoma corresponding to the tumor. • Right eye : perfectly normal. • Clinical diagnosis: Amelanotic melanoma of the chroid. Case History • • • • Gross description: 25 x 24 x 23 mm. Optic nerve was cut flush with the globe. Slightly hazy cornea: 13.5 x 11 mm. Globe transmitted light well except for a round shadow 15x15mm, posteriorly. • Eye was opened horizontally. Case History • Anterior segment was not remarkable. • Lens was in place and vitreous clear. • Arising within the choroid nasally, the posterior margin of the mass extended to the edge of the optic nerve head nasally. • The retina overlying the mass contained small amounts of pigment. Spindle cell type X10 Spindle cell type X40 • Diagnosis. – Malignant melanoma of choroid, spindle cell type ( fascicular pattern ) – Retinal invasion, – Retinal detachment. Uveal melanoma • Most common primary intraocular tumor of adult. • Arise from dendritic melanocytes of the uvea • Caucasians 8.5 x than African Americans. • Most posterior uveal melanomas present with painless visual loss • Uveal melanomas spread first to the liver Cell type Spindle cell type Epithelioid cell type Uveal melanoma • Prognostic factor – Size : Tumor height – Cell type : Epithelioid cells – Proliferative index – Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes associated with adverse outcome – Extra ocular extention – Monosomy 3 and trisomy 8 – The presence of looping pattern Case 9 Case History • 18 yo female sustained a penetrating superior limbal wound of right eye. • Next day the wound was repaired with excision of the prolapsed iris. • One month later, the patient conplained persistent pain in the right eye and failing vision in left eye. • Enunciation of the right eye were performed. X10 Dalen-Fuchs nodule Choriocapiralis Sympathetic Ophthalmia (SO) • Bilateral granulomatous panuveitis following surgical / accidental trauma to one eye, likely an autoimmune inflammatory response against ocular antigens. • Uveitis ranges from 5 days up to 50years after injury; however, over 90 % cases occur from 2 weeks to within 1 year. Sympathetic Ophthalmia (SO) • Histologic findings – – – – – – – Diffuse granulomatous uveal inflammation Eosinophils may be plentiful Plasma cells are few or moderate in number. Neutrophils rare or absent Sparing of choriocapillaris Epithelioid cells with phagocytosed pigment Dalen-Fuchs nodules • Epithelioid cells between Bruch’s membrane and retinal pigment epithelium Lens Cases Case 10 Case History • Clinical history not available. • Gross description not available. Lens x2 Thinning of nerve fiber layer Mild optic atrophy • Diagnosis – Phacolytic glaucoma Phacolytic glaucoma • Secondary open angle glaucoma – Hyper mature (White) cataract – Milky material may be seen in the AC • Denatured lens protein leak through the intact lens capsule in advanced cases and stimulates a bland macrophagic response. • Obstruction of the trabecular meshwork by macrophages that have ingested lens material and free high-molecular-weight lens protein Phacolytic glaucoma • Histologic findings – Hypermature cataract – Macrophages filled with eosinophilic lens material are seen in the aqueous fluid and on and in the iris, occluding the anterior –chamber angle. – The macrophages are not present on the corneal endothelium. References • Ocular Pathology sixth edition, Myron Yanoff Joseph W. Sassani • Eye Pathology An atlas and Basic text, Eagle • Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease 7th edition, Kumar Abbas Fausto • AFIP ATLAS OF TUMOR PATHOLOGY Series 4, Tumors of the Eye and Ocular Adnexa, Font, Croxatto, Rao Thank you!